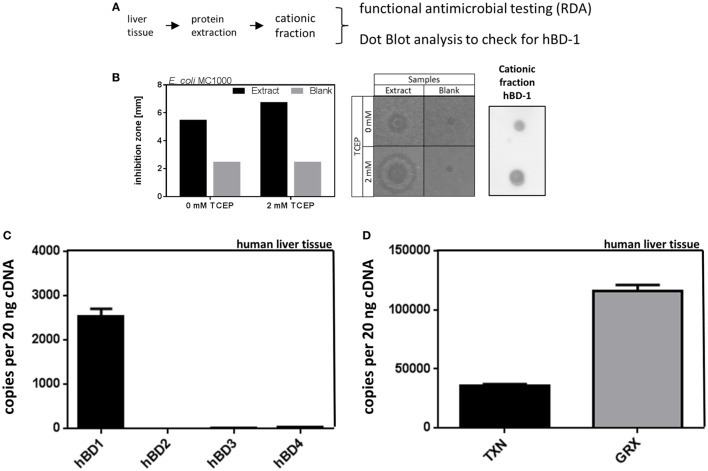
Figure 1.
Antimicrobial activity of liver protein extract is accompanied by high expression of hBD-1 and oxidoreductases in human liver tissue. (A) Schematic workflow of cationic protein extraction from liver tissue, which was tested for antimicrobial activity [radial diffusion assay (RDA)] and hBD-1 status (by dot blot analysis). (B) On the left panel, quantitative results of RDA inhibition zones of cationic protein extract and blank extract (without liver tissue) under reducing (2 mM TCEP) or non-reducing conditions (0 mM TCEP) are depicted. In the middle panel, the respective RDA results are shown as picture. On the right panel, dot blot results with hBD-1 primary antibody to confirm hBD-1 peptide in cationic protein extract are shown. (C) mRNA expression of hBD-1, hBD-2, -3, and -4 was analyzed in a human patient cohort without cholestasis or systemic inflammatory response (n = 120). mRNA transcript levels are measured in an amount of 20 ng cDNA. Total copy numbers are depicted. Data are presented as means ± SEM for each gene assay. (D) mRNA expression of TXN and GRX in human liver tissue (n = 120). mRNA transcript levels are measured in an amount of 20 ng cDNA. Total copy numbers are depicted. Data are presented as means ± SEM.