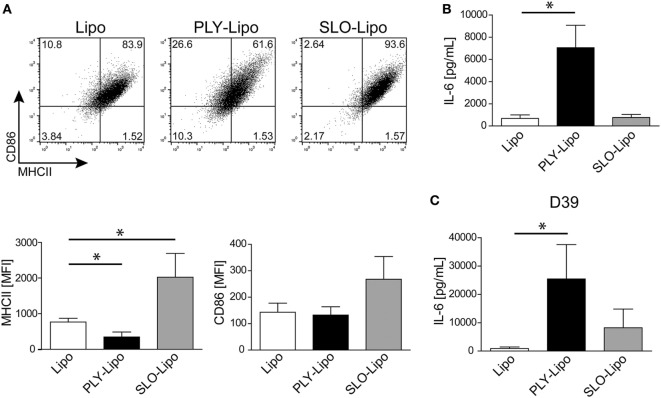
Figure 5.
Streptolysin O (SLO)-bearing liposomes-induced macrophages display a phenotype distinct from Pneumolysin (PLY)-liposome induced macrophages. Day 7 M-CSF induced human macrophages were stimulated with PLY-liposomes (PLY-Lipo) or SLO-Liposomes (SLO-Lipo) for 48 h. Equal amounts (4 µg/ml) of PLY or SLO protein were incubated with 40 µg/ml liposomes for 10 min at room-temperature before addition to the cells. (A) SLO-liposomes induce an upregulation of MHCII and CD86 in macrophages. Macrophages were stimulated with PLY-Lipo, SLO-Lipo, or liposomes without pore-forming toxin (Lipo) and analyzed by FACS gated for CD14+ cells after 48 h. Expression levels of MHCII and CD86 were evaluated compared to control cells (liposomes only; Lipo). A representative FACS blot of one of three independent experiments is shown. Mean fluorescence intensity of MHCII and CD86 of CD14+ gated cells of three independent experiments are shown (mean ± SD, n = 6; *p < 0.05, unpaired t-test, two-tailed). (B) SLO-liposomes stimulation does not induce IL-6 production in macrophages. Human macrophages were stimulated as in (A) and IL-6 production was determined after 48 h from culture supernatants performing Bio-Plex assay (mean ± SD, n = 5; *p < 0.05, paired t-test, two-tailed). (C) Re-stimulation of SLO-Lipo induced macrophages with Streptococcus pneumonia supernatants. Human macrophages were stimulated with PLY-liposomes (PLY-Lipo) or SLO-liposomes (SLO-Lipo) for 48 h. After stimulation, cell media was removed, macrophages were washed once, and re-stimulated with supernatant from S. pneumonia strain D39 for 6 h. IL-6 production was analyzed by performing Bio-Plex measurements (mean ± SD, n = 4; *p < 0.05, paired t-test, two-tailed).