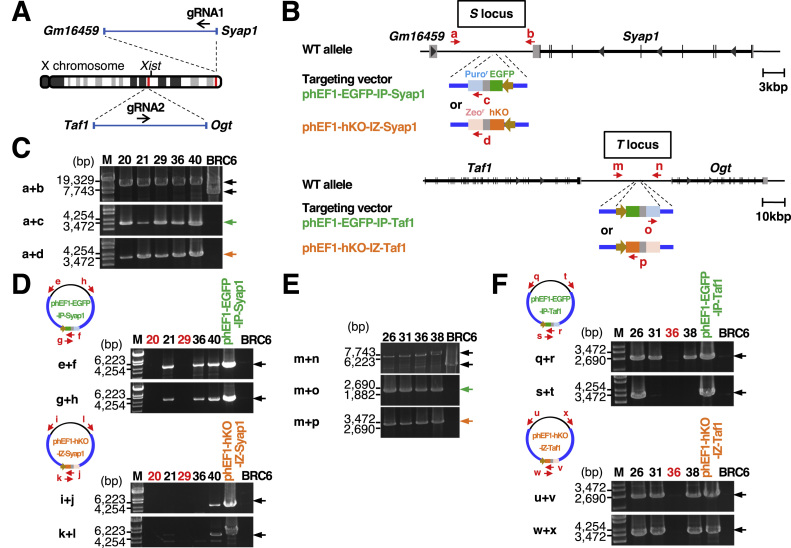
Fig. 1.
Knock-in of the EGFP and hKO genes driven by the human EF-1α promoter into the X chromosomes of mouse female ESCs. (A) Locations of the S and T loci on the mouse X chromosome are indicated by red bars. The location of the Xist gene is also indicated. The black arrows indicate the position and orientation of the guide RNAs (gRNA1 and gRNA2) used for the CRISPR/Cas9 system. (B) The intergenic sites between the Gm16459 and Syap1 genes (“S locus” in this study) and between the Taf1 and Ogt genes (“T locus” in this study) on the mouse X chromosome were chosen for insertion of the EGFP-IRES-Puror or hKO-IRES-Zeor cassette, which is driven by the human EF-1α promoter to express EGFP or hKO, respectively. The positions of the primers for genomic PCR are indicated by red arrows (a-d, m-p). (C) Genomic PCR analyses of the inserted fluorescent protein genes at the S locus in isolated ESC clones. BRC6 indicates the original female mouse ESCs used to insert the fluorescent protein genes. The primer sets used for PCR analyses are shown on the left. (D) Detection of random integration of the targeting vectors in the genome of isolated clones. The positions of primers for PCR analyses are indicated by red arrows (e-h for phEF1-EGFP-IP-Syap1, i-l for phEF1-hKO-IZ-Syap1). (E) Genomic PCR analyses of the inserted fluorescent protein genes at the T locus in isolated ESC clones. (F) Detection of random integration of the targeting vectors in the genome of isolated ESC clones. The positions of primers for PCR are indicated by red arrows (q-t for phEF1-EGFP-IP-Taf1, u-x for phEF1-hKO-IZ-Taf1).