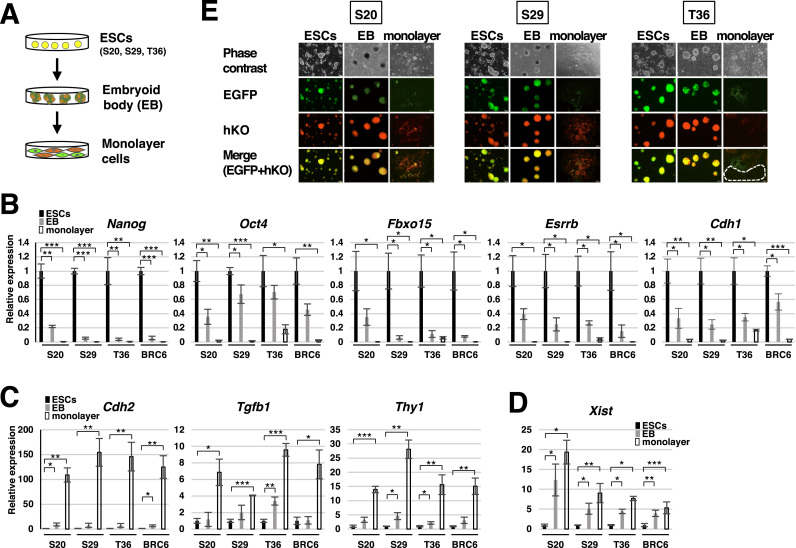
Fig. 2.
Observation of XCI in the ESCs carrying the EGFP and hKO genes on the X chromosome. (A) Differentiation of the EGFP+/hKO+ ESCs via embryoid body formation into monolayer cells and the fluorescent patters of the derived somatic cells. ESCs expressed both EGFP and hKO before differentiation, and either EGFP or hKO became inactivated randomly by XCI upon differentiation. (B-D) Expression of pluripotency marker genes (B), somatic cell marker genes (C) and the Xist gene (D) in S20, S29, and T36 clones during differentiation (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). BRC6 indicates the original female mouse ESCs. (E) Morphology and fluorescent images of the S20, S29, and T36 clones during differentiation. A white-dotted area indicates the cells that expressed neither EGFP nor hKO.