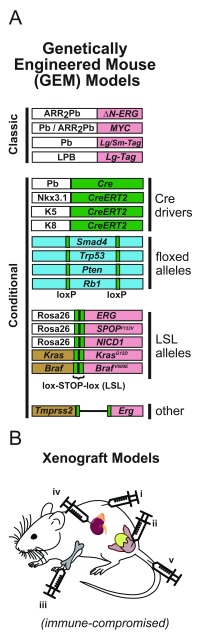
Figure 2. Overview of mouse models of prostate cancer.
( A) Genetically engineered mouse models. Classic models use the prostate-specific Probasin (Pb) or ARR 2Pb promoter to drive expression of oncogenes, including MYC 70, 71 and N-terminally truncated ERG 71. In the classic TRAMP model, Pb is used to drive expression of large and small SV40 T-antigen (Tag) 72. The LADY models use the Large Pb (LPB) promoter to drive large T-antigen only 73. Conditional models use prostate-specific Cre recombinase expression with loxP tagged alleles. Cre is most frequently driven by Probasin (Pb-Cre4 line) or a knock-in tamoxifen-inducible Cre at the Nkx3.1 locus (Nkx3-1 CreERT2 line) 74. Basal (K5) or luminal (K8) keratin promoters can been used to drive layer-specific expression in the prostate but also are expressed in other epithelial tissues 75, 76. Flanked loxP (floxed) sites can be used to induce loss-of-function deletions in endogenous tumor suppressor genes, including Smad4 77, Trp53 78, Pten 79, and Rb1 80. Lox-STOP-lox (LSL) alleles use Cre to remove an upstream STOP codon and allow expression of an oncogene. For constitutive expression, genes can be knocked-in at the ubiquitously expressed Rosa26 locus (for example, ERG 81, SPOP [ F133V] 82, Notch1 intra-cellular domain [NICD1] 83). Alternately, mutant genes can be knocked-in at the endogenous locus to maintain normal transcriptional regulation (for example, Kras [ G12D] 84 and Braf [ V600E] 85). There is also a model where loxP sites are used to delete the intergenic space between Tmprss2 and Erg, thereby mimicking the fusion observed in tumors 86, 87. Color coding: white = promoter, green = Cre or lox, blue = endogenous tumor suppressor, red = oncogene, brown = other endogenous gene. ( B) Xenograft models. Cells can be injected into immunocompromised mice via multiple methods: (i) subcutaneous, (ii) prostate (orthotopic for primary tumors), (iii) intra-tibial (orthotopic for bone metastatic tumors), (iv) renal capsule, and (v) tail vein.