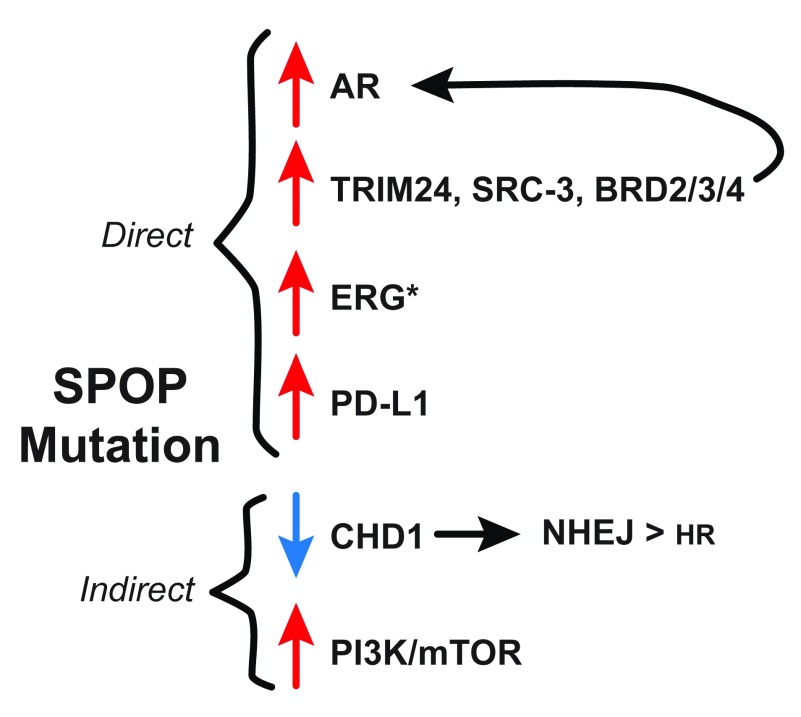
Figure 5. SPOP mutations and prostate cancer.
SPOP adapts the CUL3 E3-ligase complex to directly target and degrade AR and the AR co-activators TRIM24, SRC-3, and BRD2/3/4 170– 176. Thus, loss of SPOP increases both AR and its cofactors, leading to increased AR signaling. (*) ERG has also been reported as a direct SPOP target, although this is a debated topic 176– 178. SPOP has been shown to target PD-L1, a key target of checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapies 179. For indirect mechanisms, SPOP mutation strongly correlates with deletion of CHD1, which leads to 53BP1 stabilization and preference for error-prone NHEJ DSB repair 58, 180. SPOP mutation also upregulates PI3K/mTOR signaling via an unknown mechanism, which aids tumor growth and survival 83. AR, androgen receptor; DSB, double-strand break; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining.