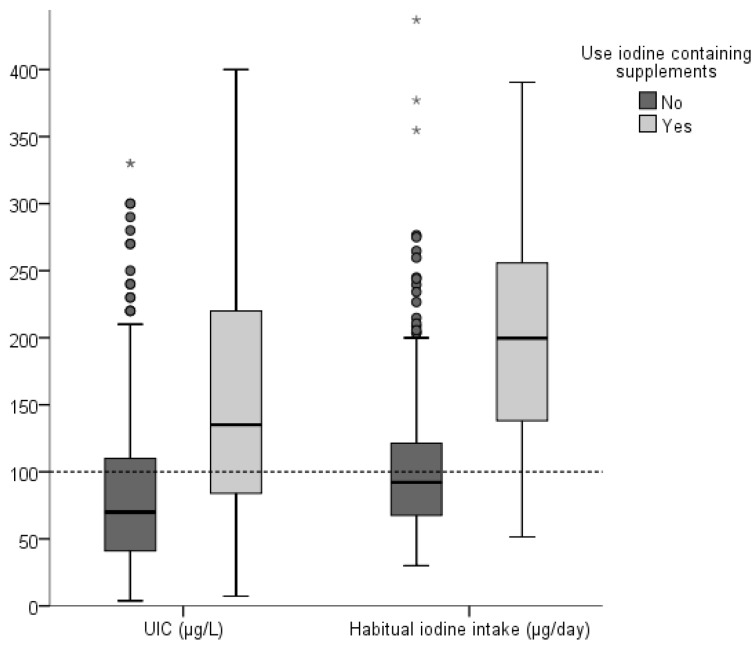
Figure 2.
Urinary iodine concentration (UIC, µg/L) and habitual iodine intake (µg/day) in iodine supplement and non-supplement users. For Box plot details see Figure 1. The points are outliers and the stars, extreme outliers. The difference in UIC and habitual iodine intake between supplement and non-supplement users was significant (p < 0.001 for both) as tested by Mann Whitney U test. The stippled horizontal line marks the World Health Organization epidemiological criteria for adequate iodine intake based on the median UIC in children and non-pregnant adults [1] as well as the average requirement (AR) for adult women by the Nordic Nutrition Recommendations (NNR). The recommended daily intake in this group is 150 µg/day [26].