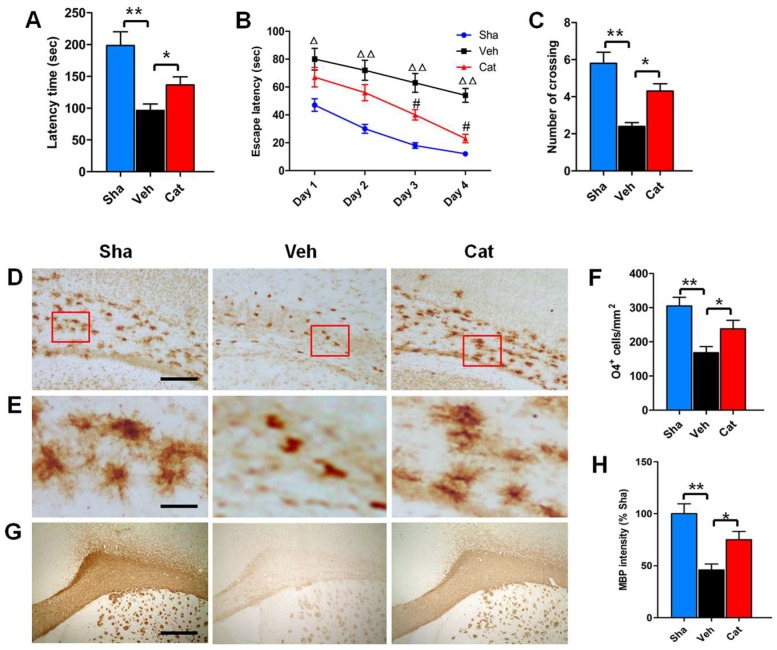
Figure 1.
Effects of catalpol on behavioral outcome, premyelinating oligodendrocytes (PreOL) damage, and myelination in a rat model of neonatal hypoxia–ischemia. (A) Rotarod test of the latency time for remaining on the cylinder in the sham-control (Sha), vehicle-treated (Veh), and catalpol-treated (Cat) groups. (B) Morris water maze test of the escape latency to find the platform in the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. (C) Number of crossings of the previous platform location in the Morris water maze test in the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. (D) Representative O4 staining in the corpus callosum of the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. Bar = 100 μm. (E) High magnification images of O4 staining in the corpus callosum of the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. Bar = 25 μm. (F) Quantification of O4-positive cells in the corpus callosum of the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. (G) Representative myelin basic protein (MBP) staining in the corpus callosum of the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. Bar = 500 μm. (H) Quantification of the optical density of MBP staining in the corpus callosum of the Sha, Veh, and Cat groups. Data are shown as means ± SEM (n = 6 in each group). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. indicated group; △p < 0.05, △△p < 0.01 vs. Sha; #p < 0.05 vs. Veh.