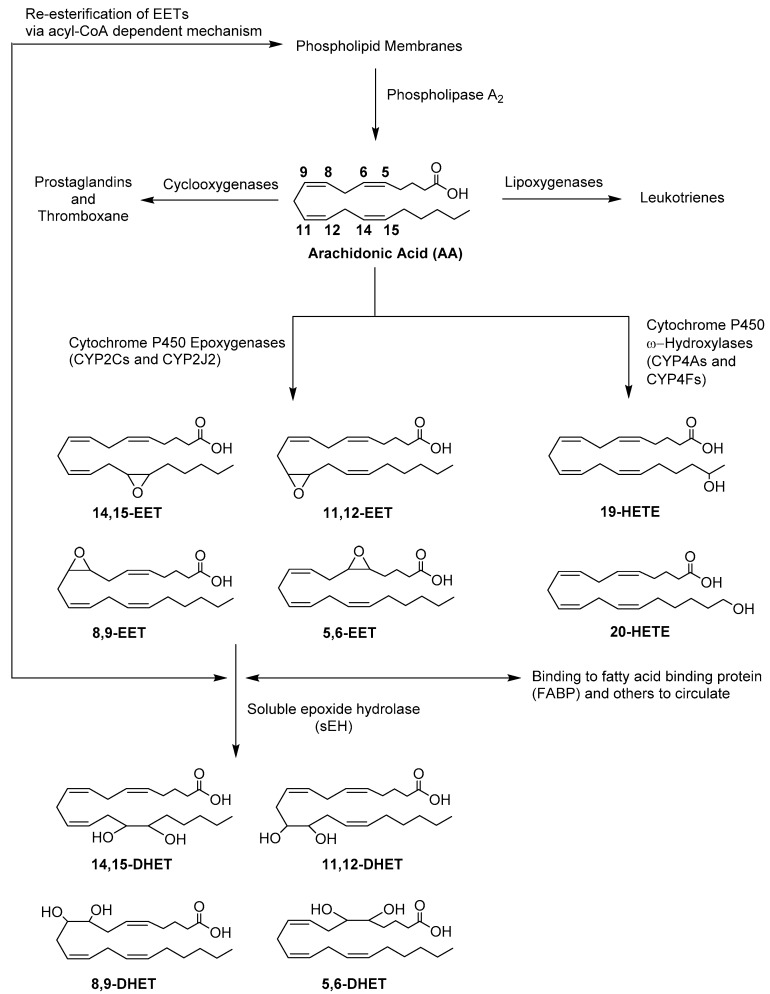
Scheme 1.
AA metabolic pathway focused on the formation of cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated eicosanoids. Upon activation of phospholipase A2, arachidonic acid (AA) is released from the phospholipid membrane. AA can be metabolized by cyclooxygenases to generate prostaglandins and thromboxane or by lipoxygenases to form leukotrienes. The CYP ω-hydroxylases, namely CYP4A and CYP4F, sub-families will convert AA to either 19-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (19-HETE) or 20-HETE, while CYP epoxygenases, namely CYP2Cs and CYP2J2, will mediate biotransformation of AA to exclusively four regioisomers of cis-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Once formed, EETs can be incorporated back into the phospholipid membrane via acyl-CoA dependent mechanism, bind to other proteins and circulate, or are hydrolyzed by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to generate dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs).