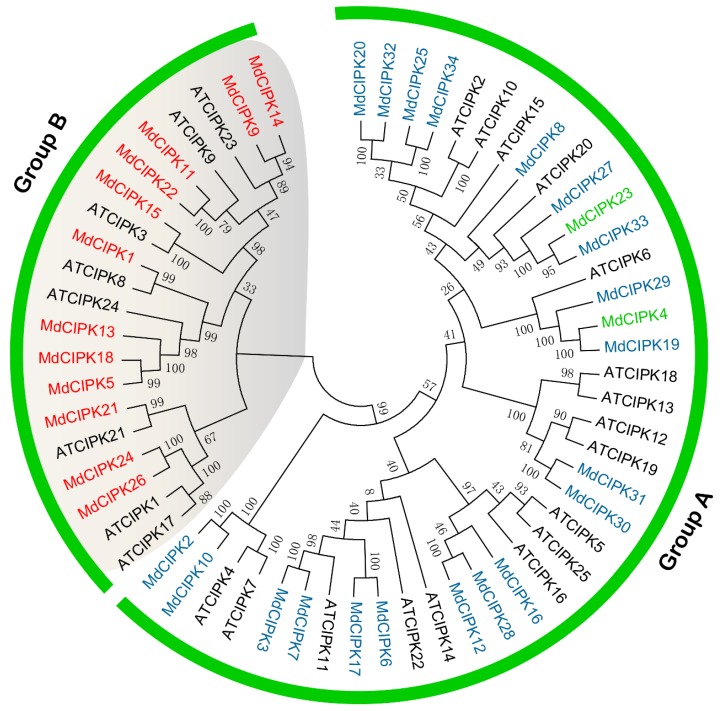
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationship of apple and Arabidopsis CIPK proteins. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor—joining method by MEGA 6.0. The bootstrap values of 1000 replicates were calculated at each node. The model was p-distance and the pattern among Lineages was Same (Homogeneous). The gaps and missing data treatment were complete deletion. The CIPK domain protein sequences, 34 from apple (MdCIPKs) and 25 from Arabidopsis (AtCIPKs, black color), were aligned by MUSCLE. The proteins were classified into 2 distinct subgroups, Group A and Group B. Red indicates MdCIPK genes with exon-poor in Group B, blue indicates MdCIPK genes with no introns in Group A, and green indicates MdCIPK genes containing introns in Group A.