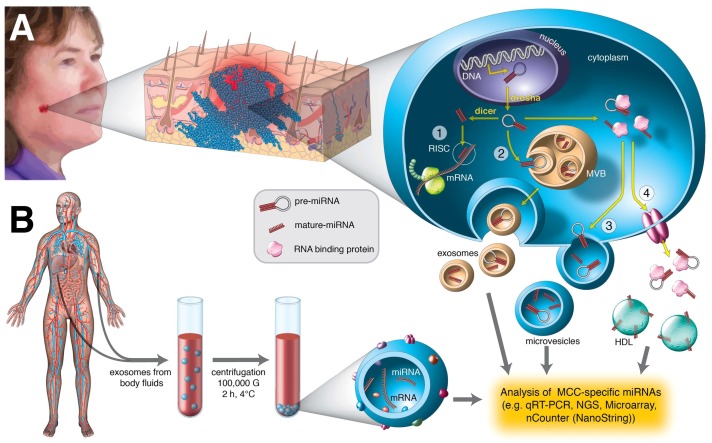
Figure 1.
Detection of MCC-specific miRNAs from tumor biopsies or from body fluids. (A) The presence of intracellular or/and extracellular MCC-specific miRNAs is examined by qRT-PCR using specific primers. Intracellular miRNAs are amplified from a total RNA isolated from MCC tumor tissue, while extracellular miRNAs are amplified from a RNA extracted from purified exosomes or from the extracellular environment. The biogenesis of a miRNA is shown. A pre-miRNA is transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and when processed to mature miRNA, it binds target mRNA (step 1). Pre-miRNAs and miRNAs can also be enclosed in vesicles and excreted in exosomes (step 2) or other extracellular vesicles (step 3). Pre-miRNAs and miRNAs can also release from the cell in complex with RNA-binding proteins, such as Argonaut 2 or nucleophosmin-1, or in complex with high-density lipoproteins (step 4); (B) circulating exosomes are purified from body fluids (e.g., blood, urine, lymphatic fluid, saliva) and a total RNA is extracted. MCC-specific miRNAs are subsequently detected by qRT-PCR applying specific primers, next-generation sequencing (NGS), microarray or nCounter.