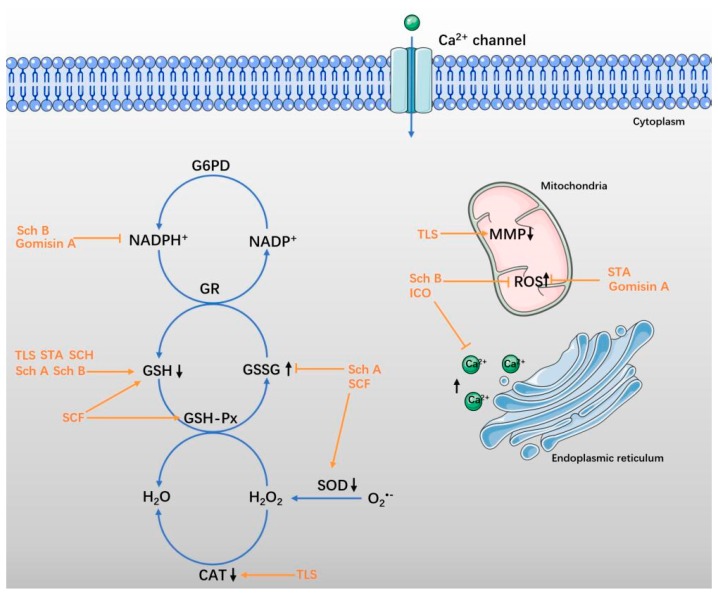
Figure 2.
SCF and its active ingredients protect against oxidative stress in neurological diseases (NDs). Under pathological conditions, the redox balance is disrupted. The degradation of glutathione (GSH) is accelerated when the GSH-Px activity is decreased, and the production of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is increased [64,65,66]. The expression of enzymes with antioxidant effects, as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), are inhibited simultaneously [67,68,69]. The mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) decreases, while reactive oxygen species (ROS) is released excessively [70,71]. Intracellular Ca2+ influx, as well as intracellular Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum are increased, resulting in a series of downstream pathological responses [72,73,74]. The protective effect of SCF and its active ingredients are shown in orange.