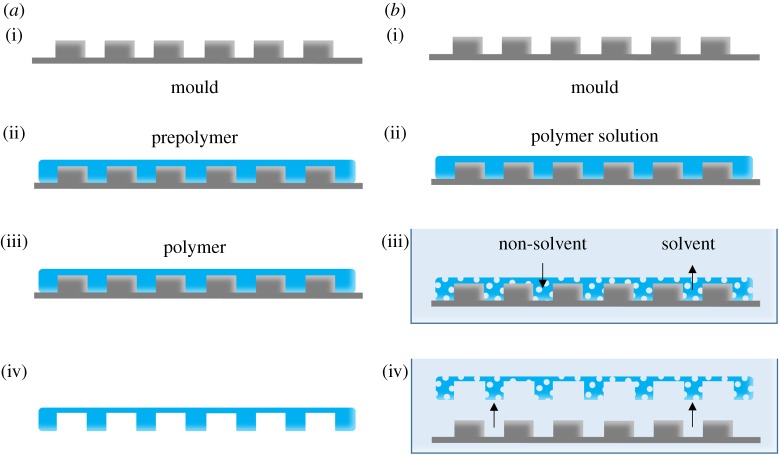
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic representation of soft lithography replica moulding. (i) A microstructured mould. (ii) The mould is filled with prepolymer. (iii) The prepolymer is then cured. Note: depending on the polymer, curing may not be necessary. (iv) Removing the mould reveals a microstructured polymer film. (b) The principle of phase separation micromoulding. (i) A microstructured mould. (ii) The mould is filled with a polymer solution consisting of polymer dissolved in a solvent. (iii) The mould and polymer solution are submerged in a bath of non-solvent. Liquid-induced phase separation occurs through the exchange of non-solvent and solvent. This exchange solidifies the polymer solution and creates pores. (iv) The porous, microstructured membrane releases from the mould. (Online version in colour.)