Table 2.
Chemical structures and properties of commonly used polymers for porous membranes in OOCs. The Tg is the temperature under which the material behaves like glass and thus is stiff. At temperatures above the Tg, polymers are more flexible. The Young's modulus is a measure of stiffness. A high modulus corresponds to high stiffness, while polymers with a low modulus are flexible. The water contact angle is the angle between a water droplet and a polymer film. Polymers with a high water contact angle are hydrophobic, while those with a low contact angle are hydrophilic. The values mentioned are contact angles measured with smooth polymer films as surface roughness changes the contact angle.
| polymer | chemical structure | Tg (°C) | Young's modulus | water contact angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| poly(dimethyl siloxane) (PDMS) | 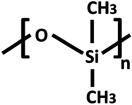 |
−125 | variable (kPa–MPa) [67] | 107.5° [81] |
| poly(bisphenol-A-carbonate) (PC) | 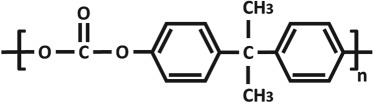 |
145 | 2–2.4 GPa | 85° [82] |
| poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) | 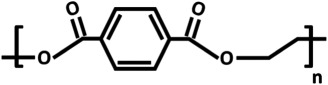 |
70 | 2–3 GPa | 82.6° [83] |
| poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | 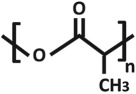 |
55–65 | 3–4 GPa | 61° [84] |
| poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL) | 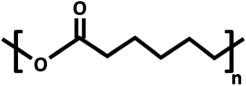 |
−60 | 400 MPa [85] | approximately 119° [86] |
