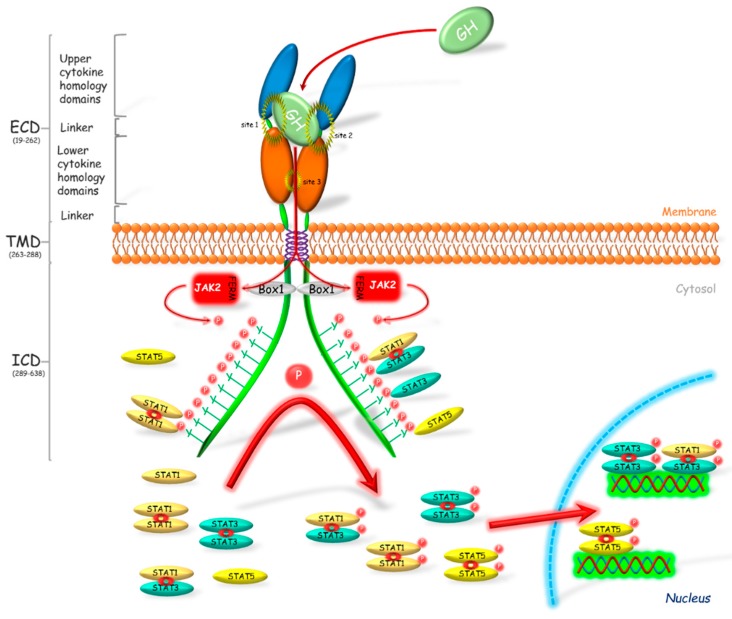
Figure 1.
Activation of the growth hormone receptor and its signal transduction. Growth hormone (GH) binds to and activates its dimerized receptor (GHR). The activation leads to JAK2 binding via N-terminal 4.1, Ezrin, Radixin, Moesin (FERM) domain to Box 1 motif of the GHR and subsequently to phosphorylation of the intracellular tyrosine residues. The phosphotyrosines provide sites for binding of the various target signaling proteins including STATs, which in consequence leads to their phosphorylation. STATs are present in the cellular cytoplasm mostly in dimerized form. After phosphorylation STATs translocate into the nucleus where these transcriptional activators bind to appropriate promoter regions on DNA, which results in the transcription of gene or a set of genes. Box 1—proline-rich domain; ECD—extracellular domain; FERM—N-terminal 4.1, Ezrin, Radixin, Moesin domain; ICD—intracellular domain; JAK2—Janus kinase 2; P—phosphorylation marker; STAT—signal transducer and activator of transcription; TMD—transmembrane domain.