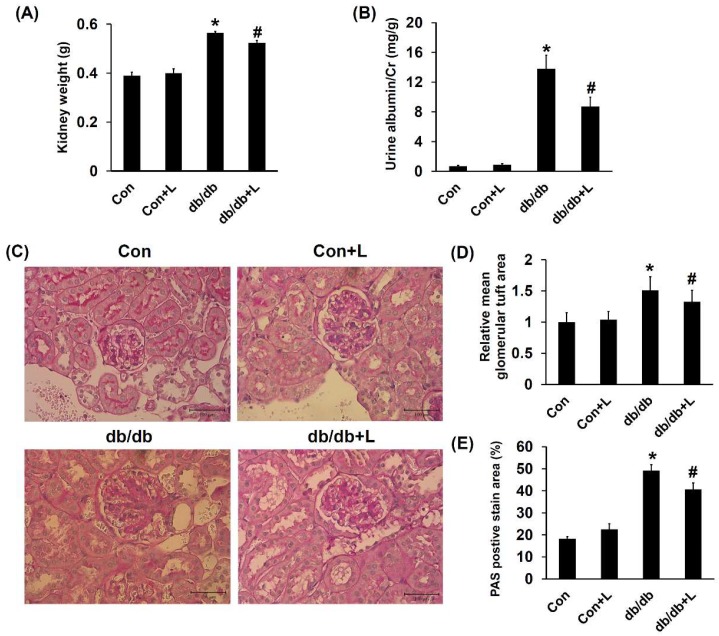
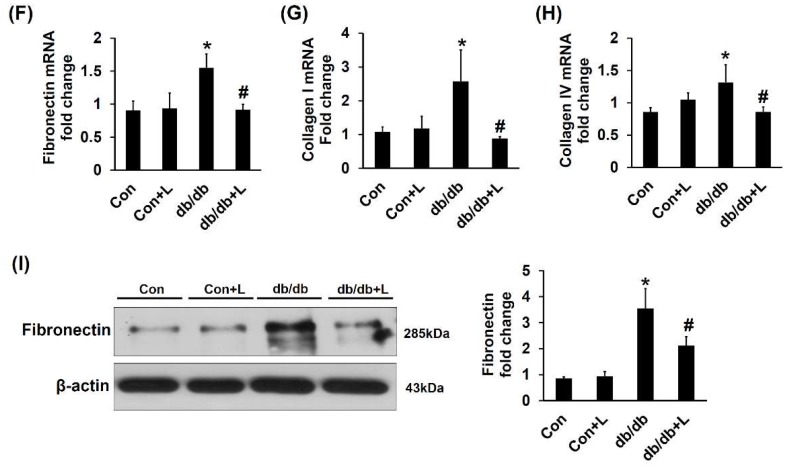
Figure 4.
Diabetic glomerulosclerosis and albuminuria in db/db mice were attenuated by dietary leucine supplementation. Mice were sacrificed, and kidneys were harvested after 12 weeks of chew diet and normal drinking water. In mice treated with leucine, 1.5% w/v of leucine was added in the drinking water. (A) Absolute kidney weights were compared in various treatment groups. (B) Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio of mice in various groups. (C) Photomicrographs illustrating PAS staining of glomeruli from mice in various treatment groups. (The scale bar shows 100μm) (D) The mean glomerular tuft area from 20 random glomeruli was analyzed, and data was presented with relative ratio to control mice. (E) The PAS staining-positive area in the glomeruli (dark red) relative to the total glomeruli area from 20 random glomeruli was analyzed. (F–H) qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of genes encoding fibronectin (F), collagen I (G) and collagen IV (H). Data are expressed as fold relative to that of the control mice. (I) Renal cortex tissue lysates were also subjected to immunoblot analysis using specific antibodies against fibronectin. Protein expression levels were quantified by densitometry and normalized to β-actin levels. Data were presented as mean ± SEM, n = 5 in Con and Con + Leu (Con + L) groups; n = 6 in db/db and db/db + Leu (db/db + L) groups. * p < 0.05, Con vs. db/db mice; # p < 0.05, db/db vs. db/db + L mice.