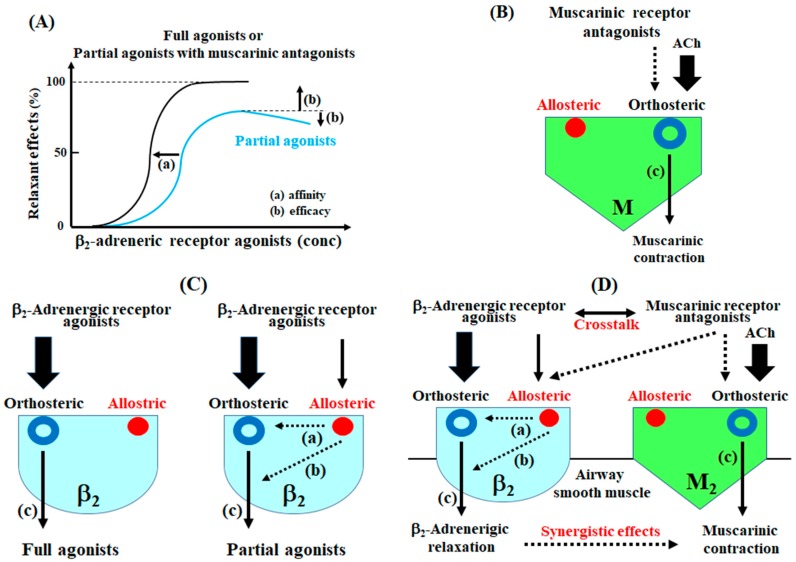
Figure 7.
Involvement of allosteric effects (affinity and efficacy modulation) in response to β2-adrenergic receptor agonists and muscarinic receptor antagonists against muscarinic contraction. (A) A schema of affinity and efficacy modulation via allosteric sites shown in concentration-response curves for β2-adrenergic receptor agonists against muscarinic contraction; (B) Muscarinic receptor antagonists inhibit muscarinic action via acting on orthosteric sites on muscarinic receptors, independent of allosteric sites; (C) Full β2-adrenergic receptor agonists do not act on allosteric sites. In contrast, partial β2-adrenergic receptor agonists act not only on orthosteric sites, but also on allosteric sites on these receptors, and these agonists reduce the signal capacity (intrinsic efficacy) of an orthosteric ligand via efficacy modulation induced by operating upon allosteric sites; (D) Muscarinic receptor antagonists act on allosteric sites of β2-adrenergic receptors, and as a result affinity and efficacy of β2-adrenergic receptor agonists are enhanced, leading to the synergistically relaxant action of the combination of β2-adrenergic receptor agonists with muscarinic receptor antagonists via crosstalk of these two receptors. M: muscarinic receptors, β2: β2-adrenergic receptors, M2: muscarinic M2 receptors. (a): affinity, (b): efficacy, (c): signal capacity (intrinsic efficacy). Arrows: activation, dotted arrows: inhibition.