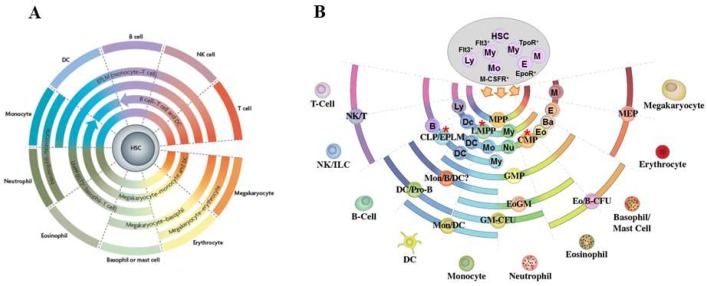
Figure 1.
A continuum or pairwise model for hematopoiesis. (A) The model envisages a continuum of fates is available to hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), with pairwise relationships between the various cell fates. The pairwise model, replaces a rigid and bifurcating lineage tree with a spectrum of fate options open to HSC. In the “classic” model, HSCs progress stepwise through a series of intermediate progenitors, to close down developmental options in a binary manner. In the new scenario, HSC make an immediate lineage choice from all of the end-cell options. The figure is, with permission, from [6] ©Macmillan Magazines Ltd. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; DC, dendritic cell; NK cell, natural killer cell. (B) The partial arcs represent the close relationships between cell lineages that we inferred from the different groups of fates that are available to known intermediary progenitor cells (marked with an asterisk). Investigators initially described Lymphoid-primed multipotent progenitors (LMPP), early progenitors with lymphoid and myeloid potential (EPLM) and common myeloid progenitors (CMP) as homogeneous population of cells. However, they are a mixture of cells with the lineage affiliations shown as cells added to the arcs for LMPP, EPLM and CMP. Affiliations include B lymphocyte (B), DC, monocyte (Mo), eosinophil (Eo), basophil (Ba), erythroid (E) and megakaryocyte (M) [16,17,18,19,20]. HSC are shown to include the following: lymphoid biased cells (Ly) [23,24] that express the fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 receptor (Flt3+) [25]; myeloid biased or committed cells (My) [26,27] that express Flt3+ [25] and/or the receptor for thrombopoietin (TpoR+) [28]; cells committed to the erythroid pathway [19] and affiliated as to expression of the receptor for erythropoietin (EpoR+) [25,29]; and cells that express the receptor for macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSFR+) and monocyte-affiliated (Mo) [25,30]. CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; CMP, common myeloid progenitor; DC/Pro-B, dendritic cell and B lymphocyte progenitor; Eo/B-CFU, eosinophil and basophil progenitor; EPLM, early progenitor with lymphoid and myeloid potential; GMP, granulocyte and macrophage progenitor; LMPP, lymphoid-primed multipotent progenitor; MEP, megakaryocyte and erythrocyte progenitor; Mon/B/DC?, monocyte, B lymphocyte and dendritic cell? progenitor; Mon/DC, monocyte and dendritic cell progenitor, NK/T, natural killer cell and T lymphocyte progenitor and NK/ILC, natural killer cell and innate lymphoid cell progenitor.