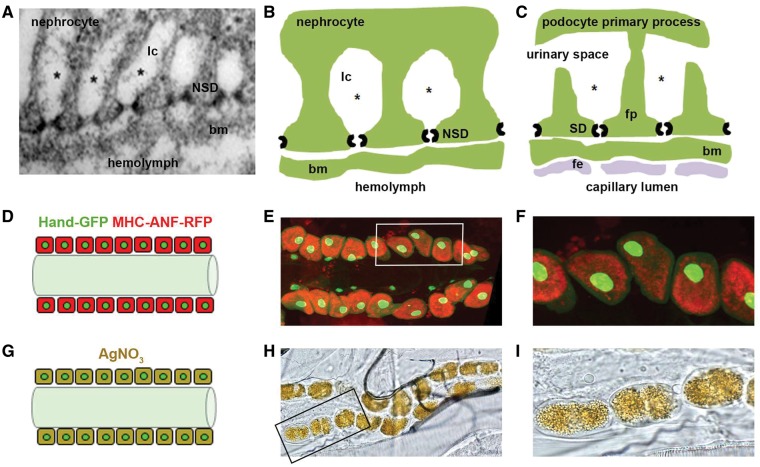
Figure 1.
Comparison of nephrocyte and podocyte basic features, and nephrocyte functional assays. (A–C). Insect nephrocytes and mammalian podocytes are structurally and functionally homologous. Panel A is a transmission electron micrograph of a Drosophila nephrocyte. Panels B and C compare structural and functional features of nephrocytes and podocytes, respectively. A basement membrane (bm) interposes a size and charge selective filtration barrier between the nephrocyte slit diaphragm (NSD) and the hemolymph of the insect open circulatory system, and the podocyte slit diaphragm (SD) and blood from the mammalian capillary lumen. In the latter case blood encounters the bm after exiting the capillary lumen through a fenestrated endothelial (fe) cell layer. The principal cellular structure in nephrocytes and podocytes mediating filtration is a slit diaphragm. In podocytes, SD proteins form intercellular filtration barriers between adjacent foot processes (fp), the intercalating termini of primary processes originating from different podocyte cells. In nephrocytes, NSD proteins form intracellular filtration barriers on either side of lacunar channel (lc) openings. In nephrocytes, filtered low molecular weight molecules (represented by *) are reabsorbed by endocytosis from the lacunar channel membrane. In podocytes the ultrafiltrate passing through the SD enters the urinary space, and is subsequently reabsorbed by proximal tubule cells. The nephrocyte therefore bears striking similarities not only to the mammalian podocyte, but is functionally homologous to proximal tubule cells as well. (D–F). Functional assay measuring nephrocyte uptake of hemolymph protein. Panel D is a schematic diagram showing pericardial nephrocytes aligned on either side of the heart tube. In this assay, muscle cells (not shown) express a MHC-ANF-RFP transgene in which a myosin heavy chain (MHC) promoter directs expression of an atrial natriuretic peptide (42) - red fluorescent protein (RFP) fusion protein. ANF-RFP is secreted into the fly hemolymph, from which it is filtered and endocytosed by nephrocytes leading to cytoplasmic red fluorescence. Hand-GFP transgene expression is visualized as green fluorescence concentrated in the nuclei of nephrocytes (shown) and cardiomyocytes (not shown). Panel E shows RFP fluorescence (54) in the cytoplasm of adult nephrocytes, reflecting endocytosis of ANF-RFP fusion protein filtered from the hemolymph. Cardiomyocytes lack red fluorescence. Green fluorescence in nephrocyte and cardiomyocyte nuclei is due to Hand-GFP expression. Panel F is a higher magnification image of cells (boxed) from panel E. (G–I). Functional assay measuring nephrocyte uptake of AgNO3. Panel G is a schematic diagram showing pericardial nephrocytes containing endocytosed and sequestered AgNO3. Panel H is a photomicrograph showing ingested AgNO3 sequestered in larval nephrocytes. Panel I is a higher magnification image of cells (boxed) from panel H.