Figure 3.
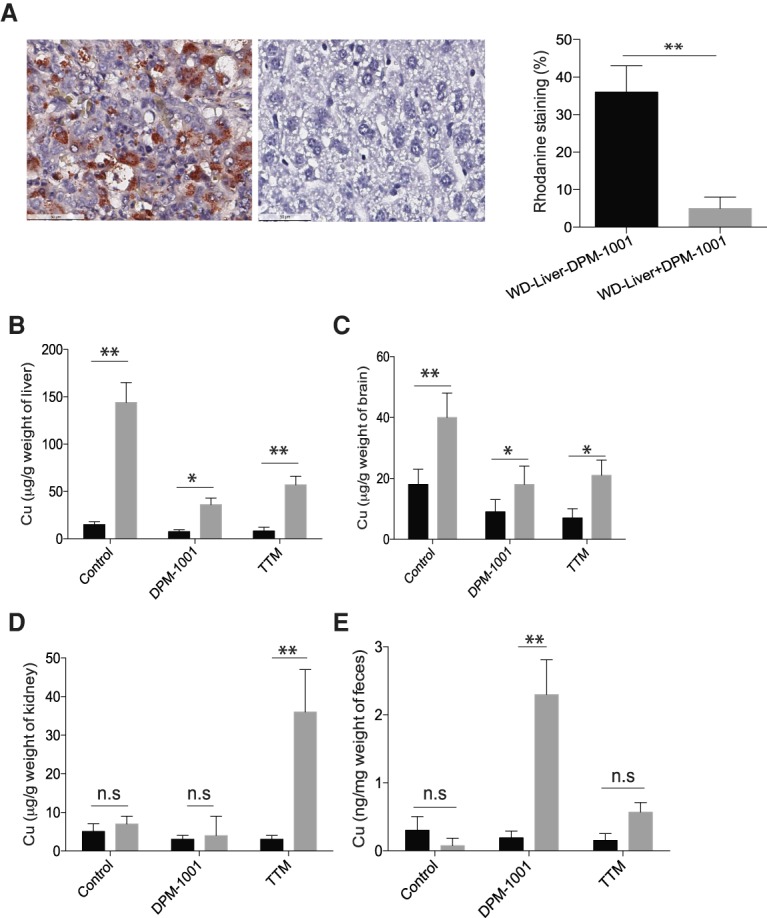
Suppression of copper levels in the toxic milk mouse model of Wilson's disease. (A) Representative sections of liver tissue from the toxic milk mouse model stained with rhodanine following treatment of animals for 2 wk with saline (left panel) or DPM-1001 (right panel). Quantitation is shown at the right. (B–D) Copper levels in the livers (B), brains (C), and kidneys (D) from wild-type (black bars) or toxic milk (gray bars) mice were measured using ICP-MS following treatment with saline, 5 mg/kg DPM-1001 orally every third day, or 5 mg/kg tetrathiomolybdate (TTM) intraperitoneally daily for 2 wk. (E) The levels of copper in the feces of these animals. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA. (**) P < 0.01; (*) P < 0.1; (ns) not significant.
