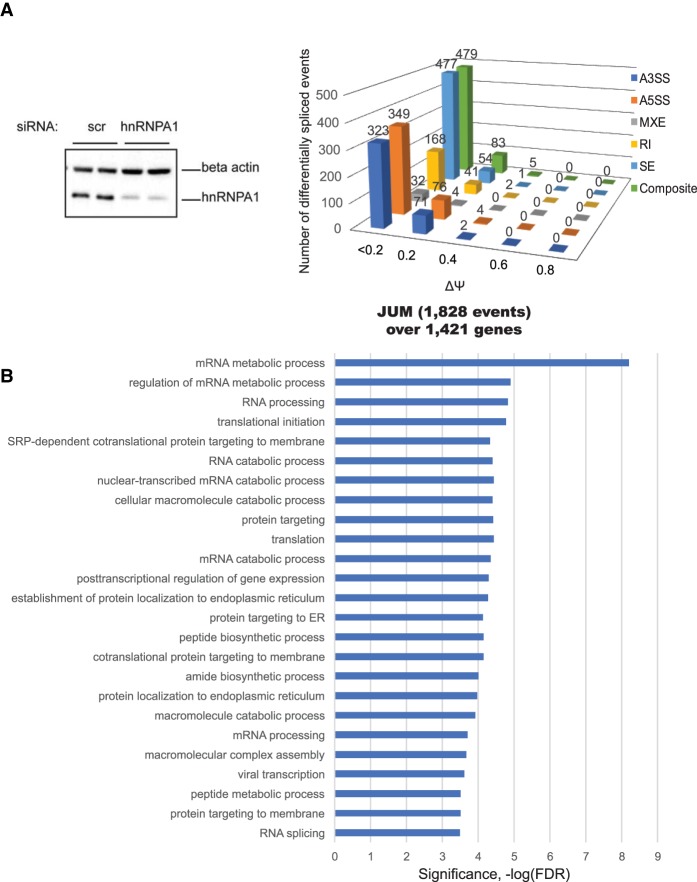
Figure 1.
Quantitation of differential AS events controlled by hnRNPA1 from RNA-seq using JUM. (A, left panel) siRNA-mediated knockdown of hnRNPA1 at the protein level. K562 cells were transfected with either nonspecific control siRNA oligos (scr si) or hnRNPA1 duplex siRNA oligos. After a second round of siRNA transfection, the cells were harvested for RNA isolation or protein lysates. (Right panel) JUM is a splicing annotation-independent method for determining pre-mRNA splicing patterns from RNA-seq data. Only splice junction-spanning reads were taken into account for quantitation. This resulted in a quantitative comparison of AS events (1828) whose splicing patterns were significantly altered in the hnRNPA1 knockdown samples versus the control (false discovery rate [FDR], P < 0.05), covering 1421 genes. The expression levels of a set of annotated events was quantitated to determine distributions over “percent spliced in” (PSI or Ψ) values. (B) Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the hnRNPA1 splicing target genes from the JUM splicing analysis against 10,043 expressed genes (reads per kilobase per million mapped reads [RPKM] > 1) in K562 cells. Categories of related genes are listed at the left, and the enrichment significance (−log FDR) is indicated along the X-axis.