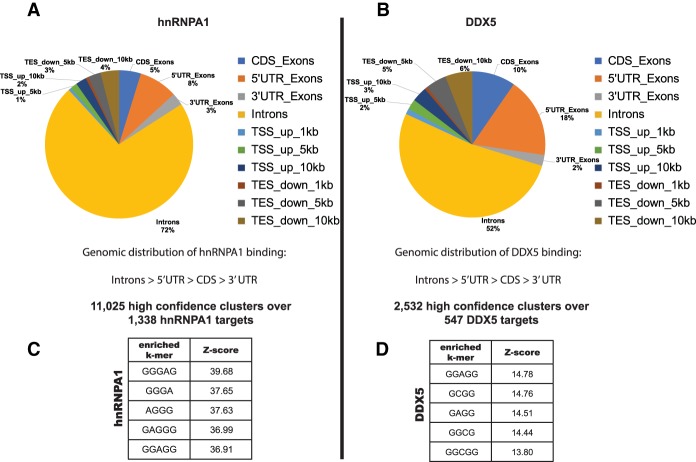
Figure 3.
Nuclear eCLIP-seq (eCLIP combined with high-throughput sequencing) for hnRNPA1 and DDX5 reveals thousands of protein-binding sites on the human transcriptome. (A,B) Pie charts showing the differential distribution of hnRNPA1- and DDX5-binding sites within different categories of genomic regions. hnRNPA1 nuclear eCLIP generated 11,025 high-confidence clusters (FDR, P < 0.05) over 1338 targets. DDX5 nuclear eCLIP generated 2532 high-confidence clusters (FDR, P < 0.05) over 547 targets. k-mer enrichment motif analysis of the eCLIP clusters is shown for hnRNPA1 (C) and DDX5 (D). Motifs were generated by extracting k-mers from reads after comparing with control data sets with reads randomly distributed over the same genomic features.