Figure 7.
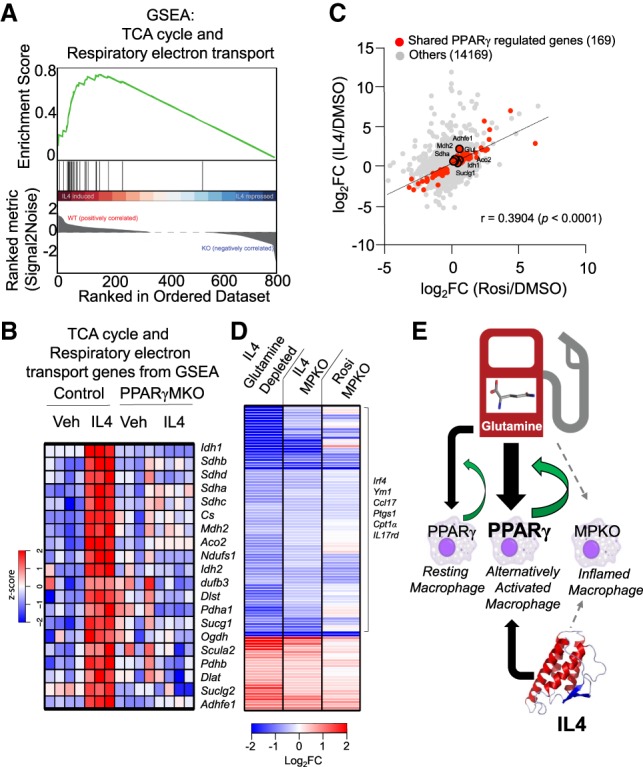
AA requires PPARγ for glutamine metabolism. (A) GSEA showing overrepresentation of TCA cycle and respiratory electron transport genes in IL4-treated controls and underrepresentation in MPKOs. (B) Heat map of z-transformed RPKM values of genes from GSEA in A in vehicle and IL4-treated control and MPKO macrophages ordered as a function of GSEA ranked metric score (high to low signal to noise ratio). (C) Scatter plot showing significant positive global correlation between Rosi-induced genes and IL4-induced genes in control macrophages. Genes in red are not induced with either Rosi or IL4 in MPKOs. (D) Heat map showing gene expression log2 fold changes of IL4-treated control macrophages in glutamine-depleted medium (vs. IL4-treated control macrophages in complete medium), IL4-treated MPKOs (vs. IL4-treated control macrophages), and Rosi-treated MPKOs (vs. Rosi-treated control macrophages). (E) PPARγ is required for glutamine-mediated AA, yet its expression is also induced by IL4. This places PPARγ at the center of a feed-forward loop for macrophage AA.
