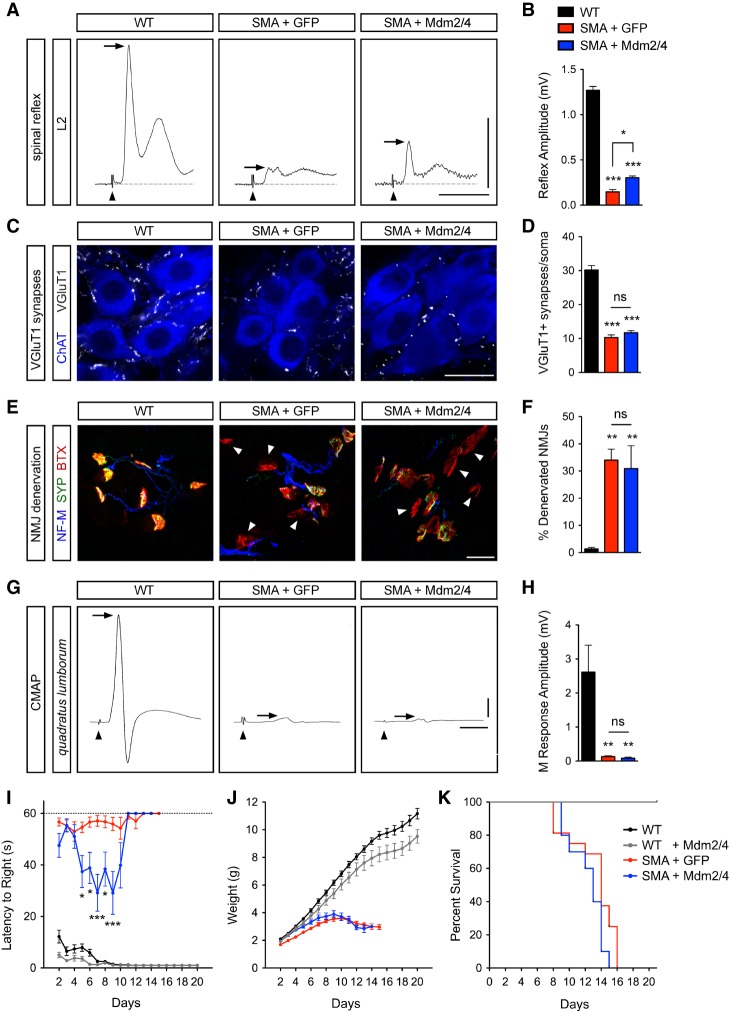
Figure 6.
Full-length Mdm2 and Mdm4 overexpression moderately improves spinal reflexes and motor behavior in SMA mice. (A) Traces of extracellular recordings of L2 ventral roots following L2 dorsal root stimulation from uninjected wild-type mice and SMA mice injected with either AAV9-GFP or AAV9-Mdm2 and AAV9-Mdm4 at P11. Arrowheads indicate the stimulus artifact. Arrows indicate the monosynaptic response. Bars, 5 msec and 0.5 mV. (B) Spinal reflex amplitudes from the same groups as in A. Data represent mean and SEM. n ≥ 3. (C) ChAT and VGluT1 immunostaining of L2 spinal segments from the same groups as in A at P11. Bar, 25 µm. (D) Total number of VGluT1+ synapses on L2 motor neuron somata from the same groups as in A at P11. Data represent mean and SEM. n ≥ 22 neurons from three mice per group. (E) Immunostaining of presynaptic (with NF-M and SYP antibodies) and post-synaptic (with BTX) terminals of neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) in the QL muscle from the same groups as in A at P11. Arrowheads indicate fully denervated NMJs. Bar, 25 µm. (F) The percentage of fully denervated NMJs in the QL muscle from the same groups as in A at P11. Data represent mean and SEM. n ≥ 3. (G) Compound muscle action potential (CMAP) traces recorded from the QL muscle following L2 ventral root stimulation in the same groups as in A at P11. Arrowheads indicate the stimulus artifact. Arrows indicate the peak of the M response. Bars, 5 msec and 0.5 mV. (H) The amplitude of the M response from the QL muscle in the same groups as in A at P11. Data represent mean and SEM. n ≥ 3. (I–K) Righting time (I), weight gain (J), and survival (K) of uninjected wild-type mice (n = 15) and wild-type and SMA mice injected with AAV9-GFP (n = 16) or AAV9-Mdm2 and AAV9-Mdm4 (n = 10) as indicated. Statistics were performed with one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test (B,D,F,H) or two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc test (I). (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001; (ns) no significance.