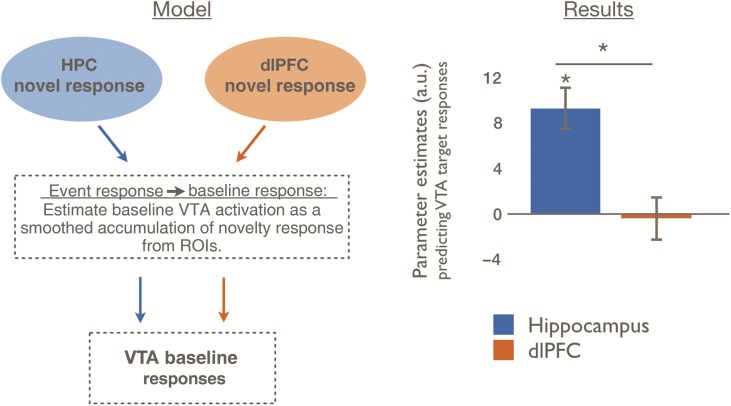
Figure 4.
Baseline VTA variability is distinctly predicted by trial-by-trial responses to novel events in the HPC, but not in the dlPFC. We estimated dlPFC and HPC contributions to VTA baseline variability by modeling the VTA BOLD signal as a smoothed accumulation of recent trial-by-trial novelty responses in each source region. For example, this model encodes the assumption that if the seed region has relatively larger trial-evoked responses to novelty for several consecutive trials, baseline VTA activation should be relatively increased during this entire period. The model derived from the HPC strongly predicted VTA activation, whereas the model derived from the dlPFC did not significantly predict VTA activation. Data are represented as means with SEM. *P< 0.001. See also Supplementary Figure 1.