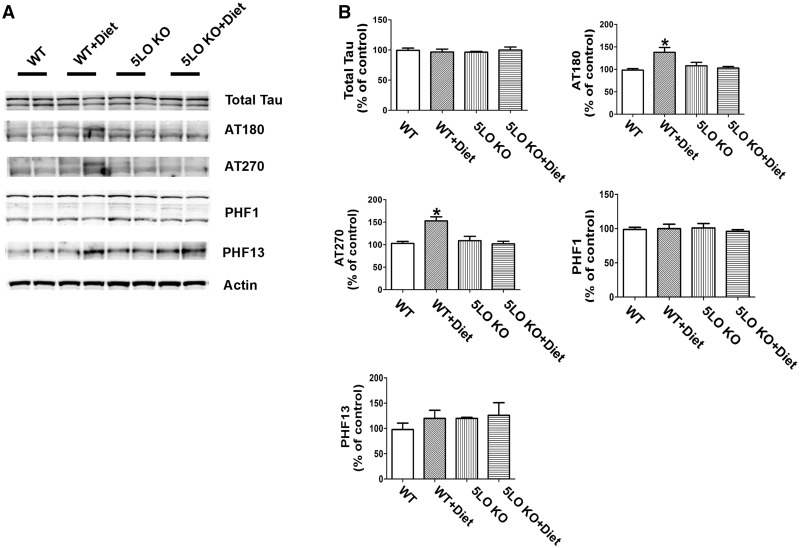
Figure 3.
Diet-induced high Hcy-dependent increase in tau phosphorylation is prevented by genetic absence of ALOX5. (A) Representative western blots of soluble total tau, phosphorylated tau at residues T231/S235 (AT180), at T181 (AT270), S396/S404 (PHF1) and S396 (PHF13) in brain cortex homogenates from wild type mice receiving regular diet (WT); wild type mice receiving folate and B vitamin deficient diet (WT + Diet); 5LOKO mice receiving regular diet (5LOKO); and 5LOKO mice receiving the Diet (5LOKO + Diet). (B) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown in the previous panel (*P < 0.05). Values represent mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5 WT-control, n = 5 WT + Diet, n = 5 5LOKO-control, n = 5 5LOKO + Diet).