Fig. 5. Analysis of monomer-dimer equilibrium of FXIIIA forms.
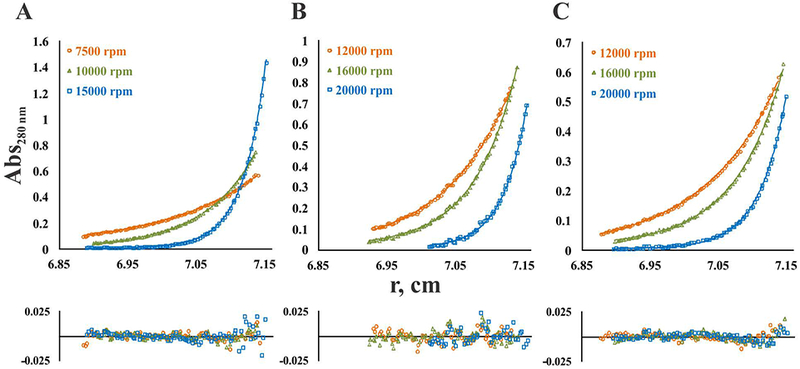
Sedimentation equilibrium profiles are presented for single loading concentration: (A) 2 μM zymogen FXIIIA; (B) 4μM FXIIIA in the presence of 100 mM CaCl2; (C) 4 μM FXIIIA activated by thrombin in the presence of 4 mM CaCl2. Experimental data (open symbols) obtained at each rotor speed (denoted on the figure panels) were fitted to a monomer-dimer equilibrium model (solid lines). Residuals are provided below the fitted data. Apparent KD-values were 8 nM for the zymogen FXIIIA, 90 mM for FXIIIA in the presence of 100 mM CaCl2, and 220 mM for the thrombin-activated FXIIIA. Global molecular weight values were 158,424 Da for zymogen, 86,801 for CaCl2-activated FXIIIA and 77,025 for thrombin-activated FXIIIA. Monte-Carlo error analysis indicated an average error for zymogen (A) of ±30 Da in molecular weight and ±0.03 for logKa, for CaCl2-activated FXIII (B) of ±40 Da in molecular weight and ±0.003 for logKa, and for thrombin-activated FXIII (C) of ±60 Da in molecular weight and ±0.002 for logKa.
