Figure 8.
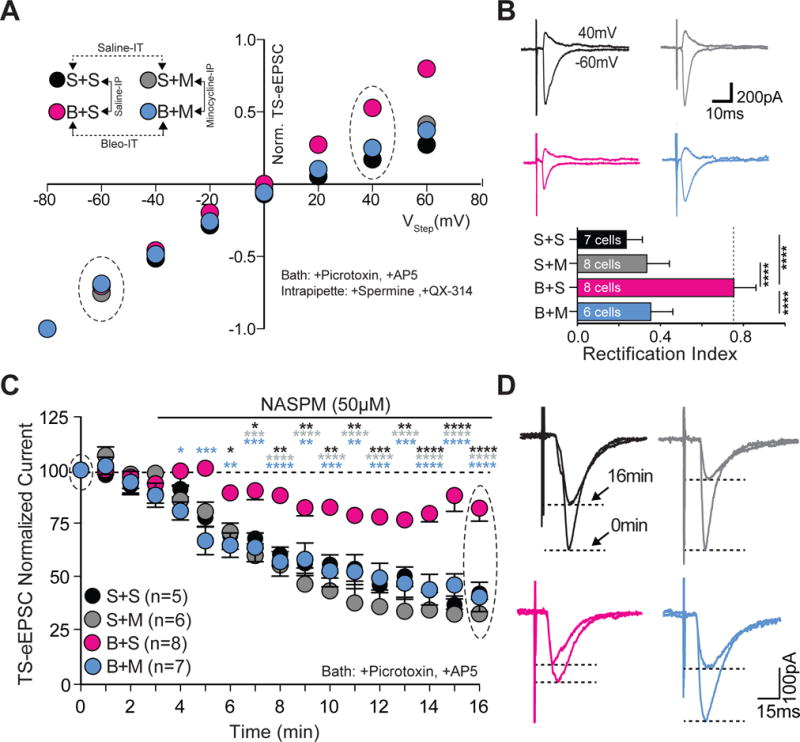
Minocycline treatment in pre-transition period lung-injured rat-pups prevents loss of current-rectification and diminished polyamine sensitivity at TS➔nTS synapses.
A Current-voltage plots for TS-eEPSCs recorded from saline-IT + saline-IP (S+S, black; n = 7 cells, 5 slices, 5 rats), saline-IT + minocycline-IP (S+M, grey; n = 8 cells/slices/rats), Bleo-IT + saline-IP (B+S, magenta; n = 8 cells/slices/rats), and Bleo-IT + minocycline-IP (B+M, blue; n = 6 cells, 5 slices, 5 rats) treated rats.
B top: Raw representative traces of TS-eEPSCs recorded at −60mV and +40 mV (circled in the I–V plot) bottom: B+M treated rats exhibited a significant reduction in the rectification index compared to B+S treated rats (****P < 0.0001), which was not significantly different from S+S (P = 0.187) or S+M treated groups (P = 0.985, One-way ANOVA and Tukey test).
C Average normalized amplitudes of TS-eEPSCs from S+S− (n = 5 cells/slices/rats), S+M− (n = 6 cells/slices/rats), B+S (n = 8 cells/slices/rats), and B+M-treated (n = 7 cells/slices/rats) rats at base line and for 13 min after bath application of NASPM (after the 3rd min). B+M treated rats exhibited significantly greater NASPM dependent depression compared to B+S treated groups at 16 min (****P < 0.0001, Two-way ANOVA and Tukey test).
D Representative raw recordings showing TS-eEPSCs at baseline (0 min) and 13 min after bath application of NASPM.
