Figure 2. Gene and Pathway Alteration Associates with Survival Predictions in Specific RCC Subtypes.
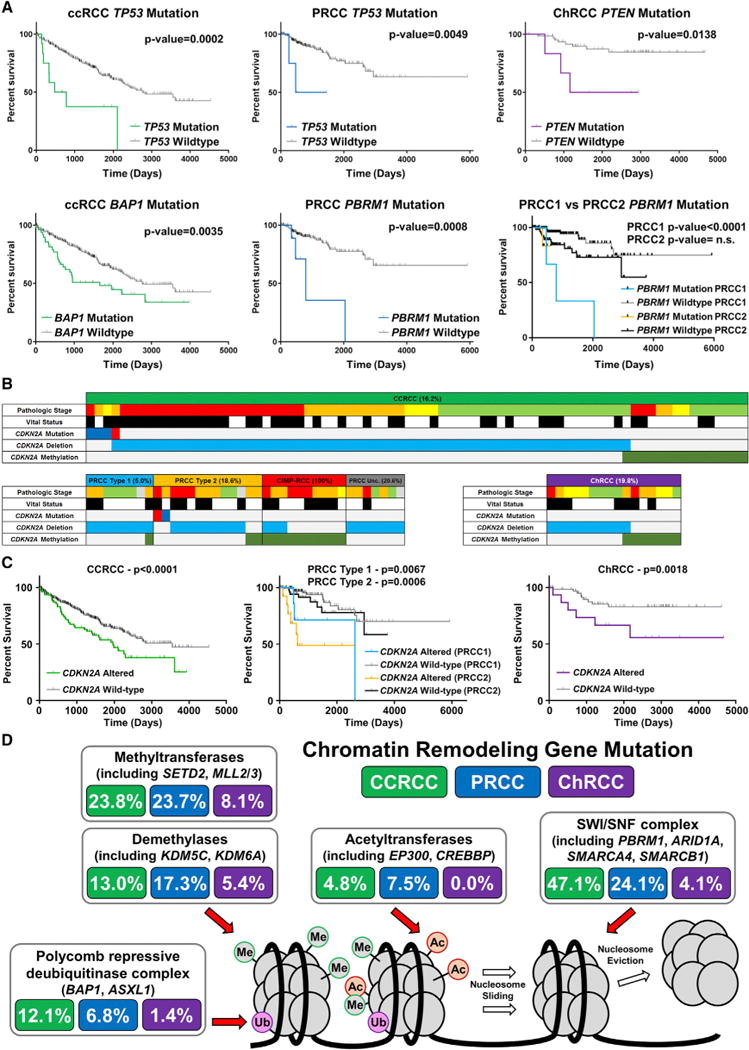
(A) Differences in patient overall survival within histologic RCC subtypes (ccRCC, green; PRCC, blue; ChRCC, purple) dependent upon gene mutation (log-rank p value). (B) Oncoprints for CDKN2A gene deletions, hypermethylation, and mutations for the histologic RCC subtypes (ccRCC, green; type 1 PRCC, light blue; type 2 PRCC, orange; Unc. PRCC, gray; CIMP-RCC, red; ChRCC, purple). Mutations were segregated into nonsense (red) and missense (blue). (C) Differences in patient overall survival within the histologic RCC subtypes (ccRCC, green; type 1 PRCC, light blue; type 2 PRCC, orange; ChRCC, purple) dependent upon CDKN2A alteration (log-rank p value). (D) Chromatin remodeling pathway mutation frequency within histologic RCC subtypes (ccRCC, green; PRCC, blue; ChRCC, purple). Abbreviations: Me, histone methylation; Ac, histone acetylation; Ub, histone ubiquitination.
