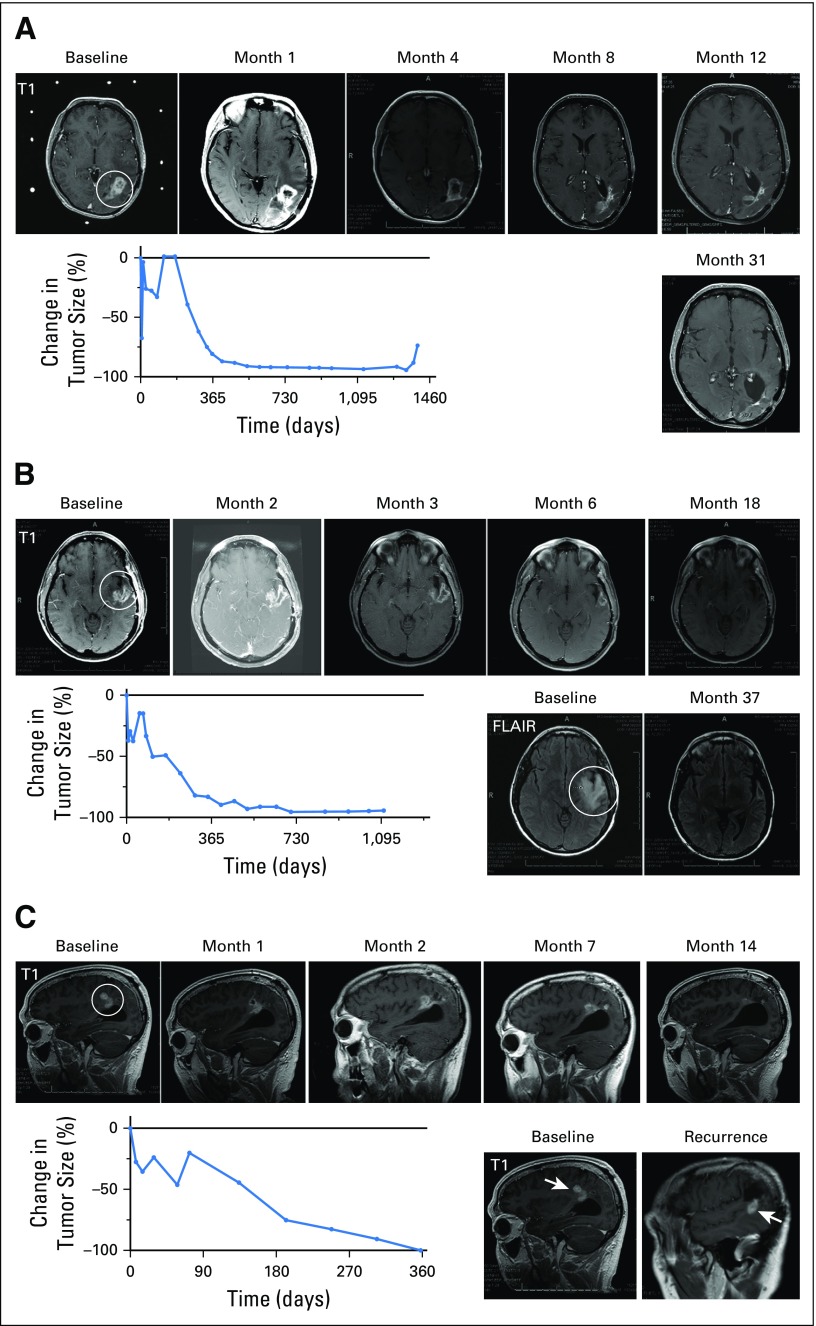
Fig 2.
Summary of the three complete tumor responses of recurrent glioblastomas after a single dose of DNX-2401. (A) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and graph of tumor size for Patient No. 12 demonstrating a complete response of a recurrent left parietal glioblastoma treated with 1 × 108 viral particles (vp) DNX-2401. Contrast enhancement was observed until 4 months post-treatment, followed by complete regression, which lasted until 41.5 months after DNX-2401 treatment. MRI scans at baseline and months 1, 4, 8, 12, and 31 after treatment are shown. Circle indicates tumor mass. The graph shows the percent change in tumor size (contrast enhancement) over time; note the initial increase in enhancement followed by a progressive decrease. (B) MRI scans and graph of tumor size for Patient No. 33 demonstrating a recurrent glioblastoma of the left superior temporal gyrus treated with 1 × 1010 vp DNX-2401. MRI scans at baseline and months 2, 3, 6, 18, and 37 after treatment are shown. Circle indicates tumor mass. Complete regression was concurrent with a decrease in peritumoral hyperintensity on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images (bottom left). As in Figure 2A, the graph of percent change in tumor size (contrast enhancement) over time shows an initial increase in enhancement followed by a progressive decrease. (C) MRI scans and graph of tumor size for Patient No. 37 with a recurrent glioblastoma of his right parietal lobe injected with 3 × 1010 vp DNX-2401. Complete regression was observed 1 year after treatment, as shown on MRIs from baseline and months 1, 2, 7, and 14. The graph of percent change in tumor size (contrast enhancement) over time shows a staggering initial increase in enhancement followed by a progressive decrease. A contrast-enhanced nodule (bottom right) arose away from the initial recurrence 29 months after DNX-2401 treatment (arrows note location of new lesion); surgical resection of this lesion revealed necrosis and inflammation and no evidence of tumor.