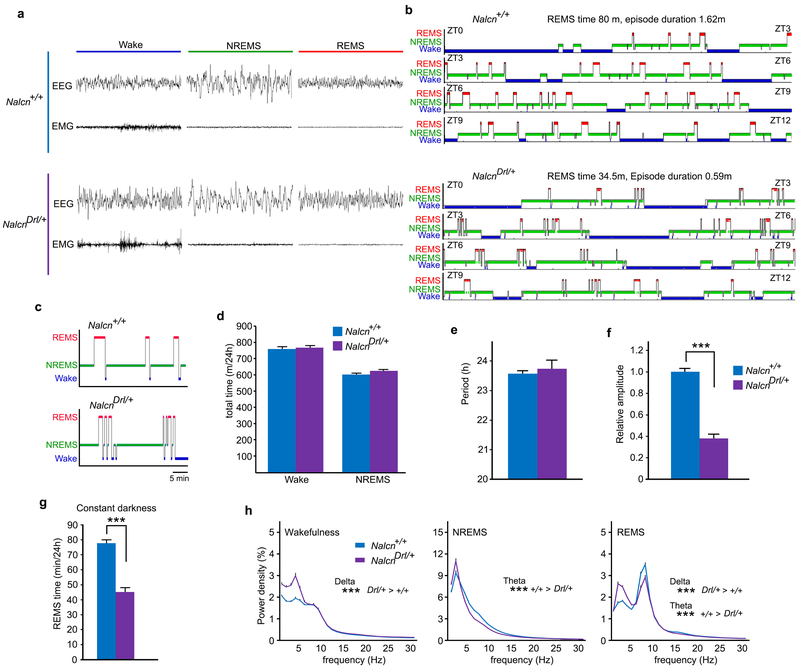
Extended Data Figure 9 |. Sleep/wakefulness behavior of Nalcn mutant mice.
a, Representative 8s-EEG and EMG for wake, NREMS and REMS of Nalcn mutant mice b, Representative hypnogram of Nalcn+/+ mice (upper) and NalcnDrl/+ mice (lower). Wake (blue), NREMS (green) and REMS (red) are indicated from ZT0 to ZT12. c, Enlarged hypnogram of around ZT7 showed the frequent transitions between NREMS and REMS of NalcnDrl/+ mice, d, Total wake time and NREMS time of NalcnDrl/+ mice (n = 29) and Nalcn+/+ mice (n = 25). Wake, P = 0.58; NREMS, P = 0.17, One-way ANOVA. e-f, Circadian period length (e) and amplitude of circadian behavior (f) in constant darkness of NalcnDrl/+ mice (n = 6) and Nalcn+/+ mice (n = 7). Two-tailed Student’s t-test, (e) P = 0.76. (f) *** P < 0.001. g, Total REMS time of NalcnDrl/+ mice (n = 9) and Nalcn+/+ mice in constant darkness (n = 8). Two-tailed Student’s t-test. *** P < 0.001. h, EEG power spectra of NalcnDrl/+ mice (n = 29) and Nalcn+/+ mice (n = 25). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. *** P < 0.001. Values are means ± sem.