Figure 5 |. Dreamless mutation in Nalcn gene increases excitability of neurons in the “REM-off” area.
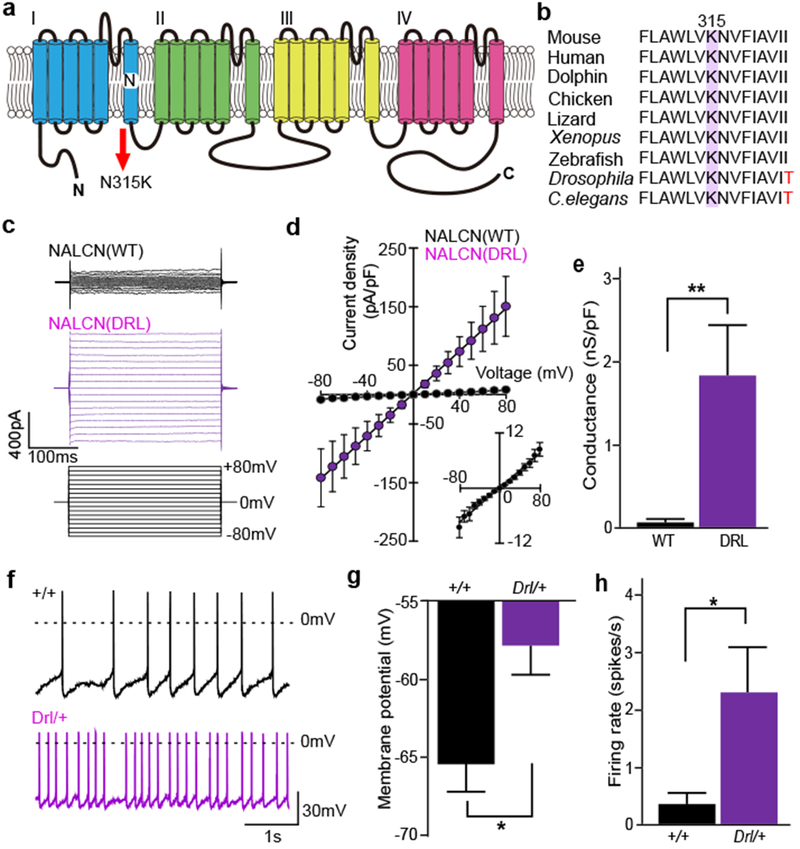
a, Schematic structure of NALCN protein. b, Phylogenetic conservation of N315 residue in NALCN. c, Representative traces of membrane currents in response to 300-ms step pulses ranging from −80 mV to +80 mV in 10 mV increments (Vh = 0 mV, lower) recorded from HEK293T cells transfected with NALCN (upper) or NALCN(DRL) (middle). d, Mean current-voltage (I-V) curves in NALCN (n = 5, black circles) or NALCN(DRL) (n = 7, purple circles and lower right). e, The conductance of NALCN(DRL)-transfected cells was larger than that of NALCN-transfected cells (NALCN, 0.09 ± 0.02 nS/pF, n = 5; NALCN(DRL), 1.81 ± 0.62 nS/pF, n = 7). Mann-Whitney Utest. ** P < 0.01. f, Representative trace of membrane potentials of DpMe neurons in Nalcn+/+ (upper) and NalcnDrl/+ mice (lower). Dashed lines indicate 0 mV level. g-h, Mean membrane potentials (g) and spontaneous firing rates (h) of DpMe neurons (Nalcn+/+, n = 33; NalcnDrl/+, n = 31). Mann-Whitney U test. * P < 0.05. Values are means ± sem.
