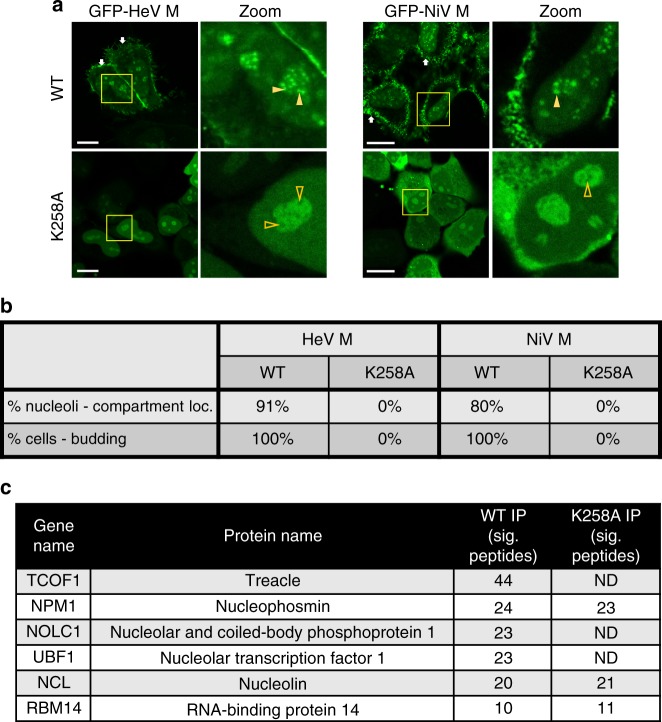
Fig. 2.
Mutation of residue K258 to alanine inhibits localization to subnucleolar compartments, binding to a subset of nucleolar proteins, and budding function of M protein. a HeLa cells transfected to express the indicated proteins were analyzed by live-cell CLSM; white arrows indicate localization of M protein at the plasma membrane/membrane protrusions; filled and unfilled yellow arrowheads indicate subnucleolar compartments with apparent accumulation and exclusion, respectively, of M protein. Scale bars correspond to 15 μm. b Images such as those in a were used to determine the percentage of nucleoli with clear accumulation of M protein in subnucleolar compartments (% nucleoli—compartment loc.; ≥447 nucleoli analyzed for each of WT and K258A-mutated HeV M protein, from four separate assays; ≥99 nucleoli analyzed for each of WT and K258A-mutated NiV M protein, from two separate assays), and the percentage of cells with localization of M protein to concentrated patches at the plasma membrane and into membrane protrusions, consistent with budding (% cells—budding; ≥83 cells analyzed for each sample from at least two independent experiments). c A subset of nucleolar interactors of GFP-HeV M and GFP-HeV M-K258A identified by IP/MS; proteins are ranked by number of significant (sig.) peptides identified; ND not detected