Figure 2. Characterization of CPS1 Conditional Knockout.
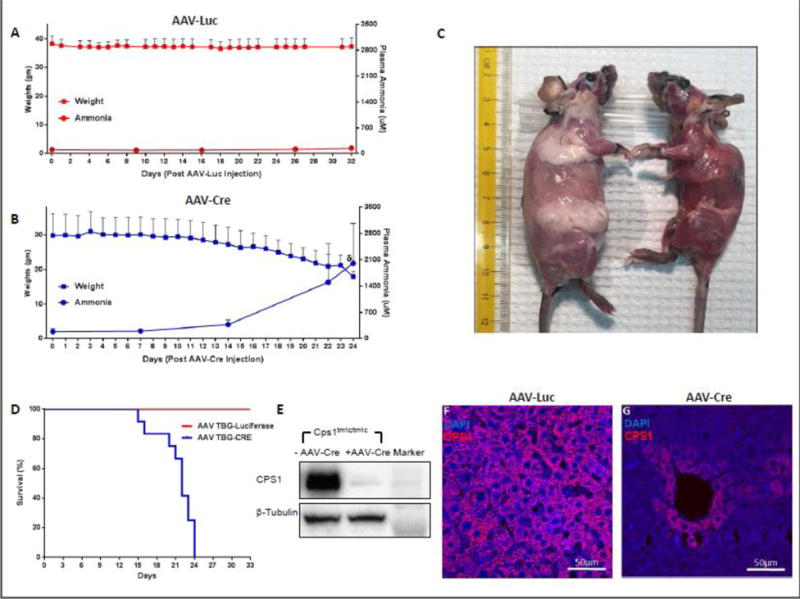
(A) Weights of control mice (n = 6) and mice with Cre-mediated disruption of Cps1 (n = 12) (B) were assessed daily, and plasma ammonia was assessed at assigned intervals. (C) Subcutaneous fat pads in CPS1 disrupted mice (right) become greatly reduced within three weeks after AAV-Cre administration (control mouse for comparison is at left). (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mice undergoing Cre-mediated Cps1 disruption compared to an irrelevant AAV control vector (AAV-Luciferase), both with a liver-specific promoter (p = 0.0002 by log-rank). (E) Western blot analysis of hepatic CPS1 expression in control and CPS1 conditionally deleted mice along with immunostaining of wild type (F) and conditionally deleted liver (G) All values are mean ± S.D. (TBG, thyroxine binding globulin) (δ refers to ammonia measured at death or when euthanized for ethical endpoint; this was not at day 26 in all animals.)
