Figure 4. Expression by helper-dependent adenovirus results in hepatic CPS1 expression.
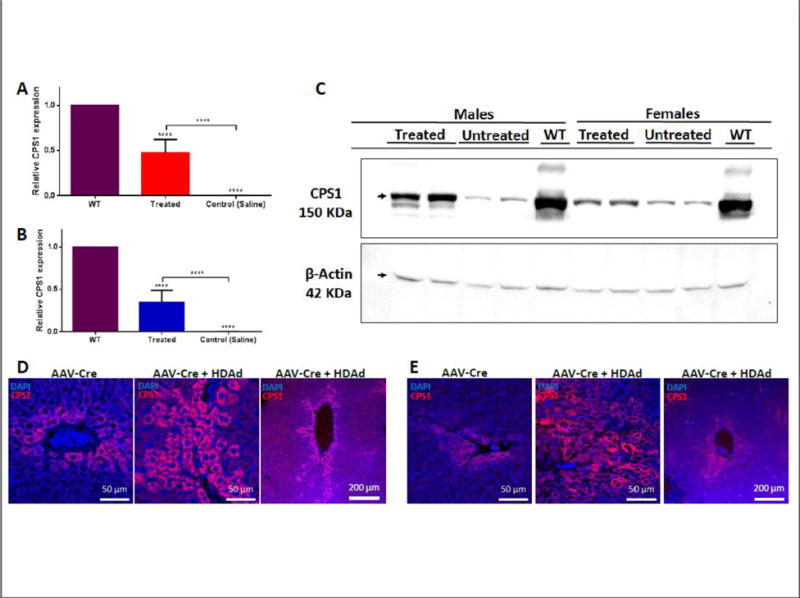
Determination of long-term relative male (A) and female (B) Cps1 mRNA expression in hepatocytes after administration of helper-dependent adenovirus (treated and untreated male and female mice, n=5 per gender; wild type males and females, n=2 per gender). Male vector- administered animals were studied at 100 days after vector administration while females were studied at the terminal time point: death or euthanized for ethical reasons. (C) Western blot of CPS1 expression in untreated mice compared to wild type mouse liver and helper-dependent adenovirus-treated mice. (Each lane represents a separate animal.) Liver immunostaining for long-term CPS1 expression after vector administration (100 days) for both male (D) and female (E) mice: left panels show remaining endogenous hepatic CPS1 expression after administration of AAV8-TBG-Cre recombinase; middle panels show expression at terminal time point (males: 100 days; females 100 days or death) after helper-dependent adenovirus expressing CPS1 administration; right panels show perivenous CPS1 from helper-dependent adenoviral expression. (All values are mean ± S.D.; ****, p ≤ 0.0001).
