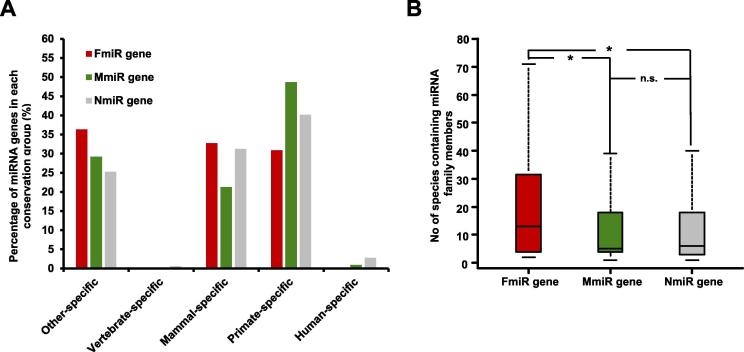
Figure 3.
The evolutionary characteristic of the sex-biased miRNA genes
A. The distribution of the FmiR, MmiR, and NmiR genes in different conservation groups. Note that miRNA genes in more conserved group (e.g., primate-specific group) do not include the miRNA genes present in less conserved groups (e.g., human-specific group). B. Comparison of the number of species in which the corresponding miRNA gene family members are present. *indicates significantly higher number of species in which the family members of FmiR genes are present, in comparison with MmiR and NmiR genes (P < 0.05), according to Wilcoxon’s test. n.s., non-significant.