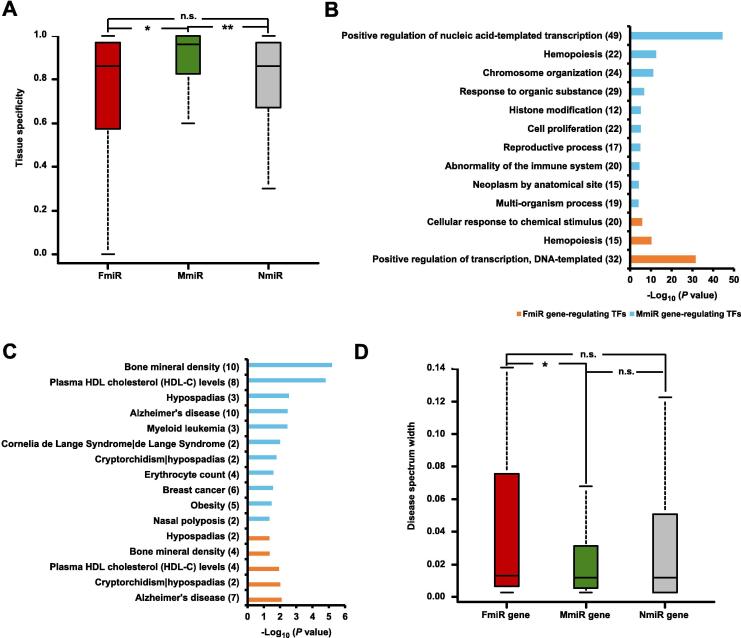
Figure 4.
The comparison of tissue expression specificity and disease spectrum width of the sex-biased miRNAs
A. Comparison of tissue expression specificity between FmiRs, MmiRs, and NmiRs. The tissue expression specificity of one miRNA is defined as the ratio of its maximum expression level among the 40 tissues examined against the total expression from all of the 40 tissues. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Wilcoxon’s test. B. The enriched functions of the FmiR-regulating TFs and MmiR-regulating TFs using the g:Profiler tool, only the top 20% significant terms (P < 0.05) are shown. Numbers in the parenthesis indicate the numbers of TFs associated with the respective functions. C. The associated diseases of the FmiR-regulating TFs and MmiR-regulating TFs using the DAVID tool (P < 0.05). Numbers in the parenthesis indicate the numbers of TFs associated with the respective diseases. D. Comparison of disease spectrum width between FmiR genes, MmiR genes, and NmiR genes. *indicates significant lower disease spectrum width of MmiR group, when compared to any of the other two groups (P < 0.05) according to Wilcoxon’s test. n.s., non-significant.