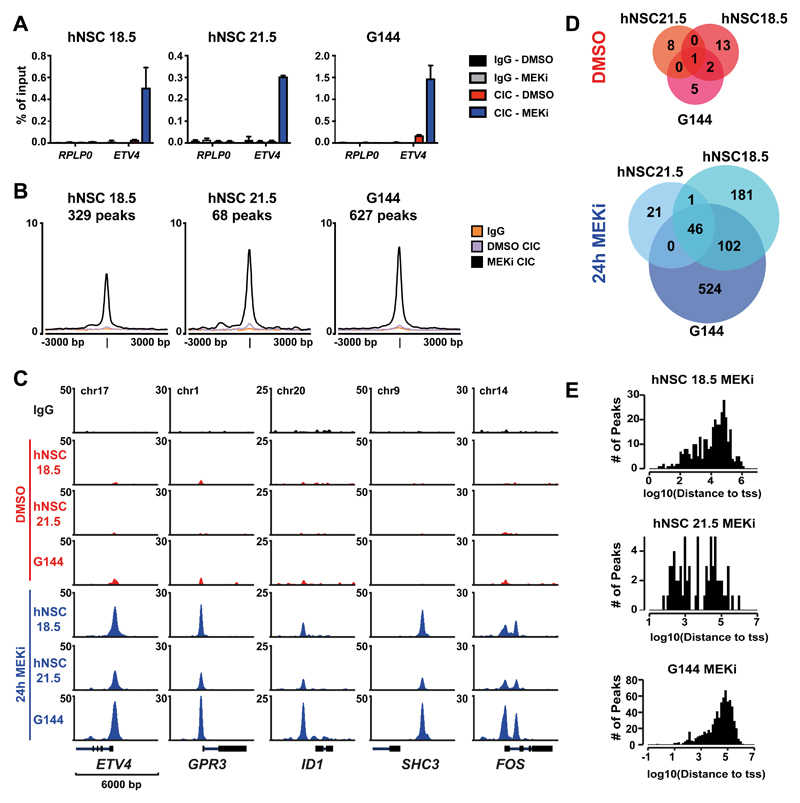
Figure 2. MAPK signaling prevents CIC from binding to its target genes.
A) ChIP-qPCR for CIC-binding at the promoter of ETV4 or control gene (RPL30) in two human neural stem cell lines (18.5 and 21.5) and one glioma neural stem cell (GNS) line (G144) after 24h mock (DMSO) or MEK inhibitor (MEKi) treatment. Data are represented as mean ±SD, n=3 B) Average intensity plot of all CIC peaks found in each cell line after 24h MEK inhibition. C) ChIP-seq tracks of CIC occupancy at selected targets genes in response to DMSO or 24h MEKi. D) Overlaps of CIC peaks detected by ChIP-seq in human neural stem cells and GNS cells with and without MEKi. E) Number of peaks found in MEKi-treated cells depicted according to their distance to the closest TSS.