Figure 3.
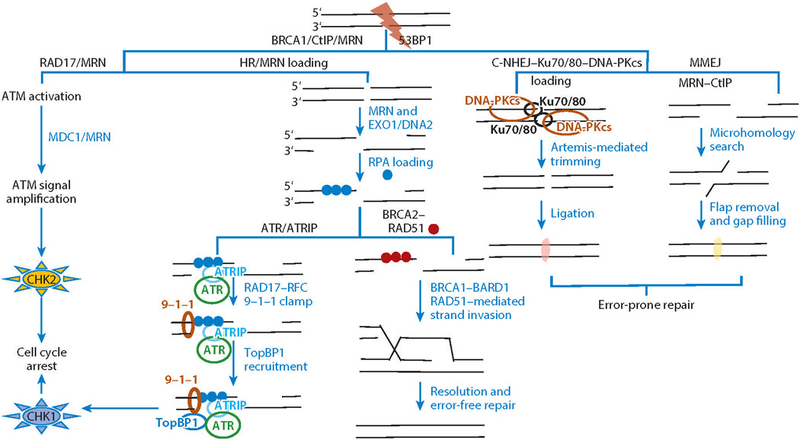
The MRN complex activates possible (alternative) pathways at DSBs. The MRN complex can initially be recruited to a DSB by RAD17 and activates the ATM kinase. Once activated, ATM phosphorylates downstream substrates including MDC1, which in turn recruits MRN, and the ATM signal is further amplified at the DSB. ATM checkpoint signaling leads to cell cycle regulation through CHK2 activation ( far left). On the basis of the cell cycle phase and nature of the DSB ends, DSBs are channeled through either HR or NHEJ for repair (central paths). In HR, the MRN complex initiates the 5΄ resection followed by long-range resection by EXO1 or DNA2. The resulting 3΄ ssDNA overhangs are loaded with ssDNA-binding protein RPA. The RPA-coated ssDNA can activate a second checkpoint pathway: ATR signaling. ATR is recruited to the RPA-coated ssDNA through ATRIP and RPA interaction. Then the RAD17–RFC clamp loading complex loads the 9–1–1 (RAD9–HUS1–RAD1) checkpoint clamp at the ssDNA and dsDNA junction on the RPA-coated ssDNA arms. The ATR activator TopBP1 is loaded by RAD9, leading to activation of CHK1 kinase and cell cycle regulation. For high-fidelity DSB repair, the BRCA2–RAD51 complex nucleates the formation of RAD51 nucleofilaments and displaces RPA from ssDNA. RAD51 nucleofilaments promote homology search and strand invasion in association with BRCA1–BARD1 for error-free HR repair through the resolution of repair intermediates. The two NHEJ pathways (right) depend upon DNA-PKcs and MRN–CtIP. In C-NHEJ, DSB ends are bluntly fused through Ku70/80–DNA-PKcs complex tethering, Artemis-mediated end processing, ligase IV, and XLF-XRCC4 scaffolding factor–mediated ligation. The C-NHEJ is independent of the MRN complex; however, MMEJ operates through MRN–CtIP-mediated resection followed by priming based on microhomology, flap removal, and gap filling. Abbreviations: ATM, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; ATR, ataxia-telangiectasia and RAD3-related; ATRIP, ATR-interacting protein; C-NHEJ, canonical nonhomologous end joining; DNA-PKcs, DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit; DSB, double-strand break; HR, homologous recombination; MMEJ, microhomology-mediated end joining; MRE11, meiotic recombination 11 homolog 1; MRN, MRE11–RAD50–NBS1 complex; NBS1, Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein 1; NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; RAD50, DNA repair protein RAD50; RFC, replication factor C; RPA, replication protein A; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA.
