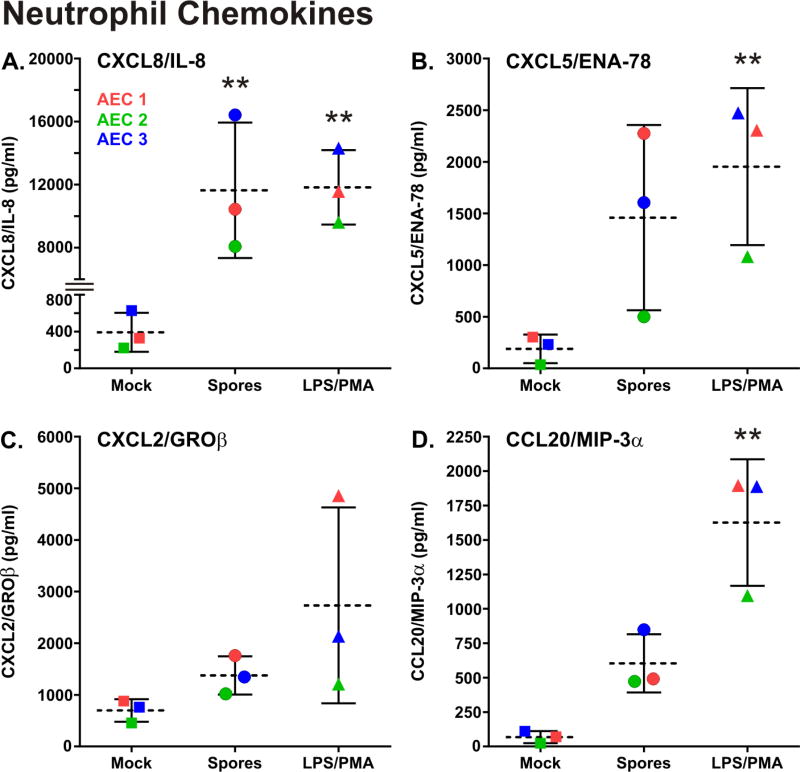
Figure 4.
B. anthracis spore exposure induces neutrophil chemokine production in primary human type I-like AEC. AEC were exposed for 24 hours to 1 × 106 cfu/ml of B. anthracis spores (circles), mock treated (squares) or exposed to LPS/PMA (1µg/ml and 0.1µg/ml, respectively) which served as a positive control (triangles). The media supernatants were harvested and the amount of neutrophil chemokine proteins in the media supernatants was measured by fluorescent multiplex or individual colorimetric sandwich ELISAs. The results from each of the three AEC donors is shown (donor 1 = red, donor 2 = blue, and donor 3 = green) and the data is expressed as the means (dashed line) ± SD. Means were compared to data for the mock (negative control) group, and statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA using Tukey multiple comparisons test. ** p ≤ 0.01.