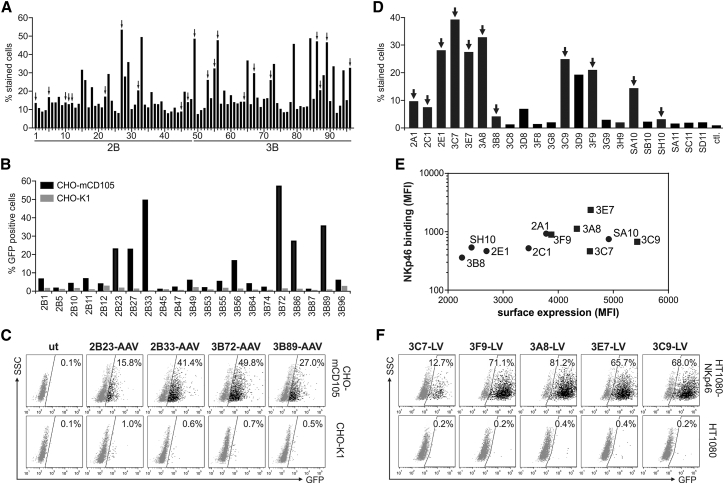
Figure 8.
Selection of CD105 and NKp46-Specific DARPins for Receptor-Targeted Gene Transfer
B-N2C and B-N3C DARPin libraries were used to select binders specific for murine CD105 and DARPin libraries VV-N3C and S-N3C for the selection of binders specific for the NK cell marker NKp46. (A and D) Crude E. coli extracts of randomly picked clones obtained as output of the ribosomal display selection procedure for CD105 (A) and NKp46 (D) were analyzed for binding to HT1080 cells overexpressing the corresponding target receptor (HT1080-CD105, A; HT1080-NKp46, D) via flow cytometry. The percentage of cells bound by the DARPin clone is shown. Arrows indicate selected DARPins used for further analysis. For CD105, 96 (A) and for NKp46, 22 (D) individual E. coli extracts were analyzed. ctl, control E. coli extracts without DARPin. (B) 21 out of 96 identified CD105-binding DARPins were cloned into the expression plasmid pDARPin-VP2 and used to produce CD105-targeted AAV particles encoding GFP for transduction of CD105-positive (CHO-mCD105) and -negative (CHO-K1) cells. Cells were analyzed for GFP expression 72 hr post-transduction by flow cytometry. (C) Representative dot plots of four selected CD105-AAV particles from (B). The percentage of GFP-positive cells is indicated. ut, untransduced cells. (E) 11 identified NKp46-binding DARPins were cloned into the expression plasmid pCG-HΔ18-DARPin. Surface expression of the H-fusion proteins after transient transfection of HEK293T cells and binding of recombinant NKp46 were analyzed via flow cytometry. Correlation of the surface expression of the corresponding DARPin-H fusion protein and binding to recombinant NKp46 is shown. DARPins used for gene transfer experiments in (F) are indicated by rectangles. (F) HT1080-NKp46 and parental HT1080 cells were incubated with NKp46-DARPin displaying LV particles encoding GFP as indicated. Cells were analyzed 72 hr after transduction by flow cytometry. The percentage of GFP-positive cells is indicated.