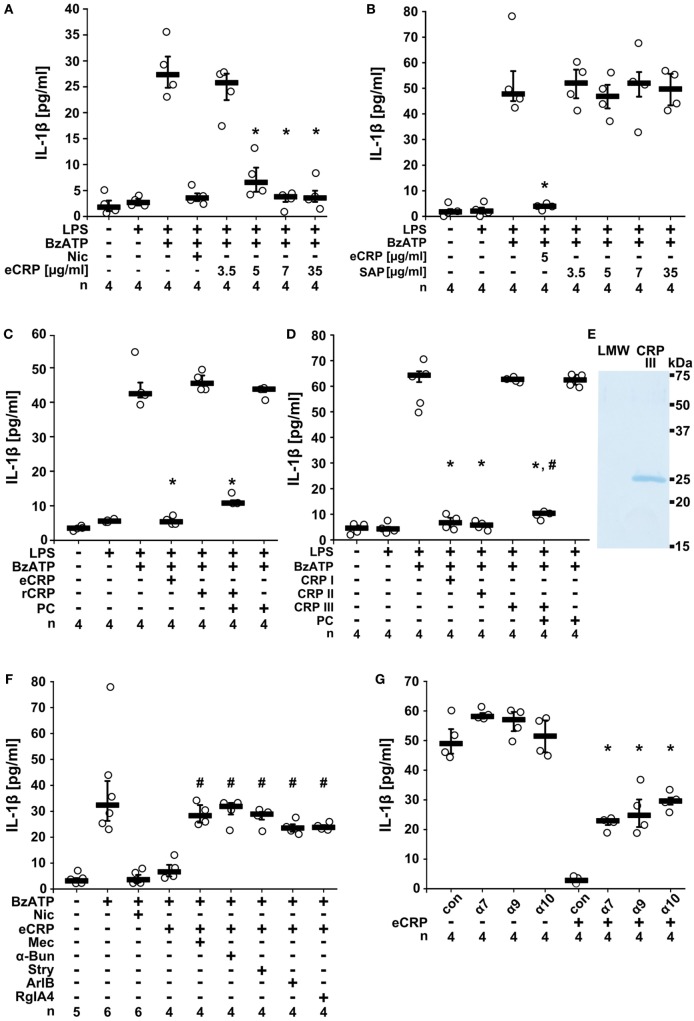
Figure 1.
Purified human endogenous C-reactive protein (eCRP) inhibits BzATP-induced release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) from U937 cells. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-primed (1 µg/ml, 5 h) U937 cells were stimulated with BzATP (2′(3′)-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine 5′-triphosphate triethylammonium salt; 100 µM) and IL-1β was measured 30 min later in cell culture supernatants. (A) eCRP dose-dependently inhibited the BzATP-induced IL-1β release, nicotine (Nic; 100 µM) served as a positive control. (B,C) Serum amyloid P (5 µg/ml), human recombinant CRP (rCRP) (5 µg/ml), or low concentrations of free phosphocholine (PC) (1 µM) did not impair IL-1β release, but a combination of rCRP and PC (1 µM) did. (D) The inhibitory effect of eCRP (CRP I; 5 µg/ml) was preserved after ultrafiltration (cutoff 10 kDa; CRP II), but abolished by ultrafiltration in the presence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (1.1 mM; CRP III). PC (1 µM) reconstituted the activity of CRP III, whereas 1 µM PC alone was ineffective. (E) CRP was retained in CRP III and absent from the low molecular weight fraction (LMW). SDS-PAGE followed by staining with Brilliant Blue. (F) The effect of eCRP was reversed by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) antagonists mecamylamine (Mec; 100 µM), α-bungarotoxin (α-Bun; 1 µM), strychnine (Stry; 10 µM), ArIB (500 nM), and RgIA4 (200 nM). (G) In experiments using small interfering RNA (siRNA), silencing of the nAChR subunits α7, α9, and α10, but not control siRNA (con) attenuated the inhibition by eCRP. Data are presented as individual data points, bar represents median, whiskers encompass the 25th to 75th percentile. *p ≤ 0.05, different from LPS-primed cells stimulated with BzATP alone. #p ≤ 0.05, different LPS-primed cells were stimulated with BzATP and eCRP. Kruskal–Wallis followed by Mann–Whitney rank sum test.