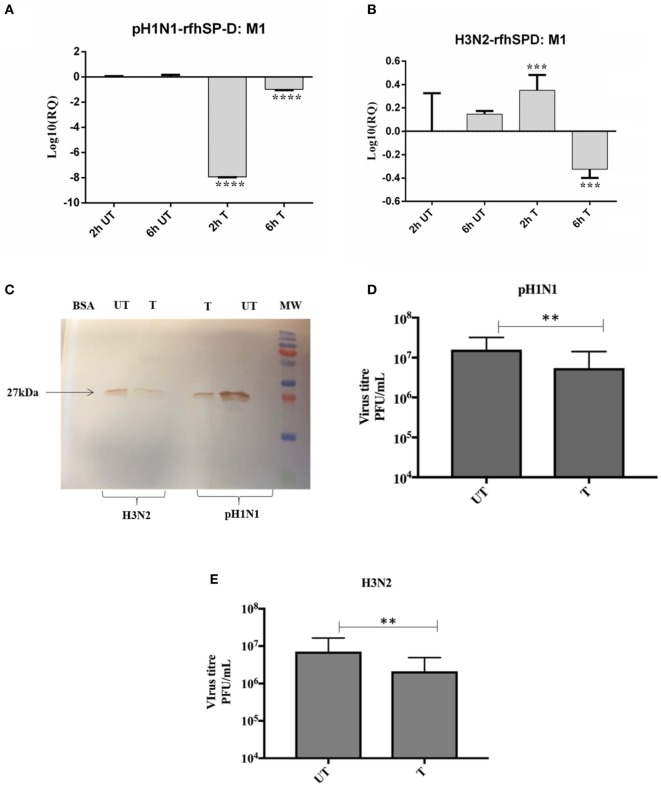
Figure 5.
rfhSP-D restricts replication of (A) pH1N1 and (B) H3N2 in target human A549 cells. M1 expression of both pH1N1 and H3N2 influenza A virus (IAV) (MOI 1) after infection of A549 cells at differential time points at 2 and 6 h. A549 cells were incubated either with pre-incubated pH1N1 and H3N2 with (10 µg) or without purified rfhSP-D. Cell pellets were harvested at 2 and 6 h to analyze the M1 expression of IAV. Cells were lysed, and purified RNA extracted was converted into cDNA. Infection was measured via qRT-PCR using M1 primers and 18S was used as an endogenous control. Results shown are normalized to M1 levels at 2 h untreated. Significance was determined using the unpaired one-way ANOVA test (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001) (n = 3). (C) Western blotting to shown M1 expression in both untreated (cells + virus) and treated (cells + virus + 10 µg/ml rfhSP-D) following 6 h incubation. Titration assay to show the anti-IAV activity of rfhSP-D (10 µg/ml), using both pH1N1 (D) and H3N2 (E) subtypes. A549 cells were infected with pH1N1/H3N2 (MOI 1) for 24 h. Then, the supernatants were collected and virus titers measured using a TCID50 assay. Treatment with rfhSP-D reduced viral titers by approximately 40%, suggesting that rfhSP-D acts as an entry inhibitor.