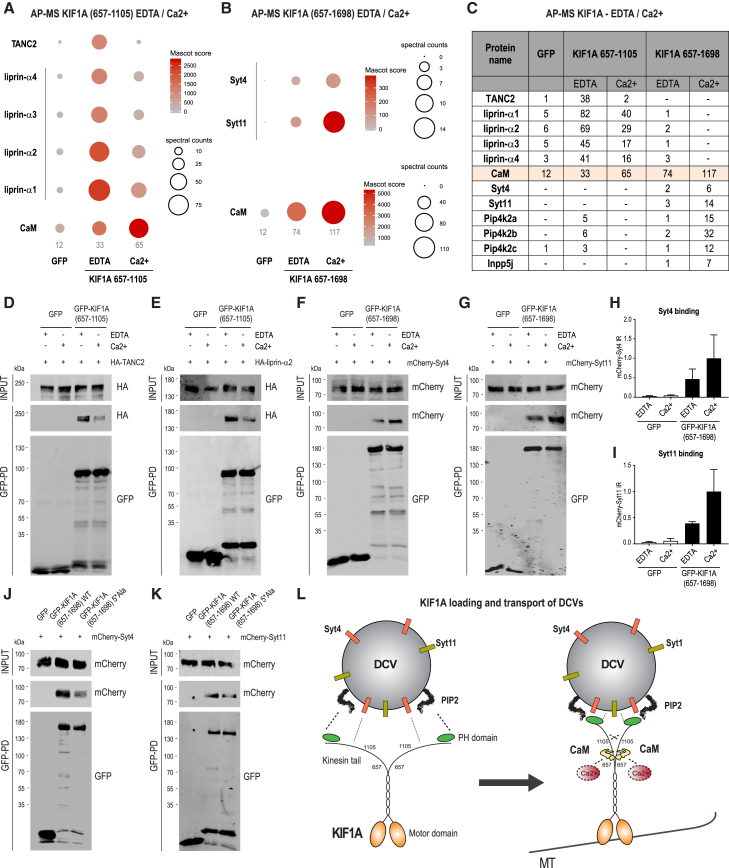
Figure 3.
KIF1A Binds DCVs in a Ca2+/CaM-Dependent Manner
(A) bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1105) was purified using streptavidin pull-downs and incubated with rat brain extracts in the presence of 2 mM EDTA or 2 mM Ca2+. KIF1A(657-1105) interactors were identified by MS. Mascot scores and spectral counts of selected proteins (TANC2, liprin-α, and CaM) are graphically represented by colors and spheres, respectively. See also (C) and Figure S2A.
(B) bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1698) was incubated with rat brain extracts in the presence of 2 mM EDTA or 2 mM Ca2+. KIF1A(657-1698) interactors were identified by MS. Mascot scores and spectral counts of selected proteins (Syt4, Syt11, and CaM) are graphically represented by colors and spheres, respectively. See also (C) and Figures S2B–S2E.
(C) Table represents the number of spectral counts detected in AP-MS experiments of bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1105) and bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1698) in the presence of 2 mM EDTA or 2 mM Ca2+ for selected co-purified proteins: TANC2, liprin-α, calmodulin (CaM), synaptotagmin (Syt), phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinase (Pip4k2), and inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (Inpp5).
(D and E) bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1105) was incubated with protein extracts of cells expressing HA-TANC2 (D) or HA-liprin-α2 (E) in the presence of 2 mM EDTA or 2 mM Ca2+. WB detection was performed using HA and GFP antibodies.
(F and G) bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1698) was incubated with protein extracts of cells expressing mCherry-Syt4 (F) or mCherry-Syt11 (G) in the presence of 2 mM EDTA or 2 mM Ca2+. WB detection was performed using mCherry and GFP antibodies.
(H and I) Quantifications of Syt4 (H) and Syt11 (I) relative intensities shown in (F) and (G), calculated as the ratio of co-purified mCherry signals normalized on the bioGFP-KIF1A. n = 3 experiments per condition. The bars show mean ± SEM.
(J and K) bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1698_WT) or bioGFP-KIF1A(657-1698_5∗Ala) was incubated with protein extracts of cells expressing mCherry-Syt4 (J) or mCherry-Syt11 (K). WB detection was performed using mCherry and GFP antibodies.
(L) Schematic model illustrating the Ca2+-CaM mechanism acting on the KIF1A tail, leading to DCV loading and mobilization.