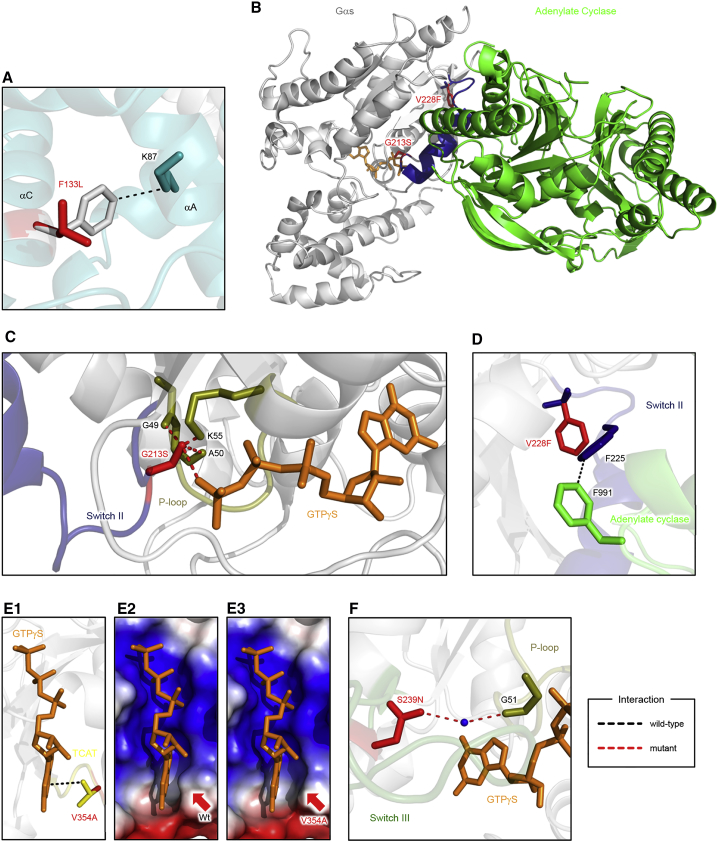
Figure 3.
Structural Basis of Molecular Effects of F133L, G213S, V228F, V354A, and S239N Mutants
(A) F133L mutation disrupts a cation-π interaction between F133 and K87.
(B) Modeling the effects of G213S and V228F mutations on the crystal structure of Gαs-AC5 complex (PDB: 1AZS).
(C) G213S mutation introduces hydrogen bond network with γ phosphate of GTPγS (orange) and three P loop residues (olive).
(D) Predicted effects of V228F mutation on the organization of Gαs-AC5 complex.
(E) V354A mutation eliminates a hydrophobic interaction with a guanine ring of a nucleotide (E1). Comparison of wild-type (E2) and V354A (E3) by electrostatic surfaces shows the broadening of nucleotide-binding pocket in the mutant.
(F) S239N mutation introduces a water-mediated hydrogen bond with G51 in a P loop (olive). Please refer to detailed descriptions in the main text.
See also Figure S2.