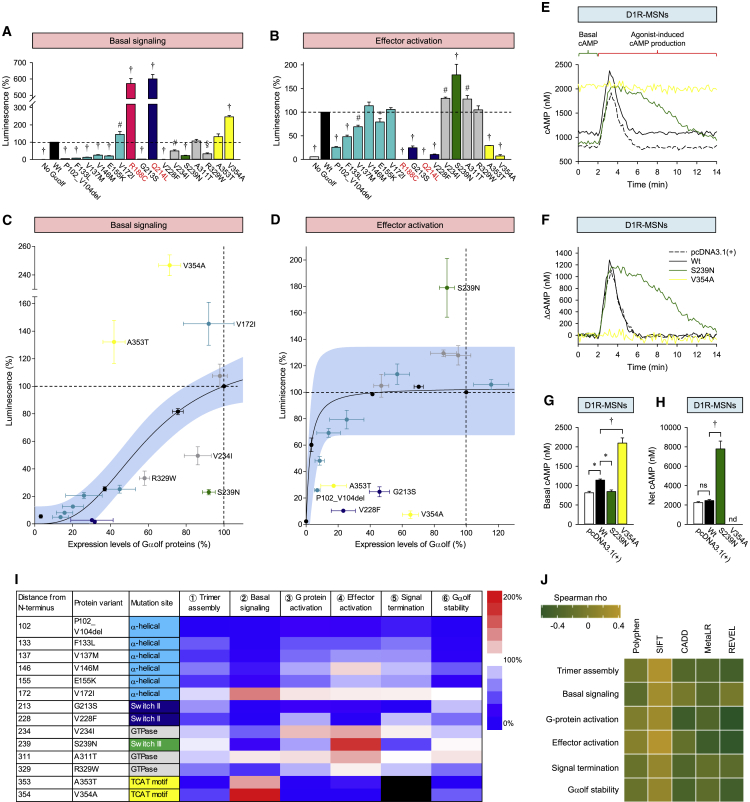
Figure 5.
Effects of Mutations on Coupling to Adenylyl Cyclase and Functional Classification of Dystonia
(A and B) Effect of mutations on basal cAMP levels (A) and agonist-induced cAMP production (B) measured with GloSensor-22F cAMP sensor.
(C and D) Correlation analysis of basal cAMP (C) and agonist-induced cAMP production (D) with expression levels of Gαolf measured by quantitative western blotting.
(E) Representative cAMP response of D1R-MSNs to 100 μM dopamine applied in a phasic 1 s burst at 2 min time point measured with the TEPACVV sensor genetically encoded in CAMPER mice.
(F) Normalized response from data in (E) highlighting kinetic aspects of cAMP responsiveness upon dopamine application.
(G) Quantification of the basal cAMP concentration.
(H) Quantification of the net cAMP change by calculating area under the curve in response to dopamine application.
(I) Meta-analysis of signaling changes caused by mutations in Golf’s function combining data of all assays and measurements.
(J) Heatmap showing Spearman’s rank correlation between different predictive measures of deleteriousness and experimental measures. The correlations were not statistically significant, after correcting for multiple testing using Benjamini-Hochberg method (false discovery rates).
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.