Figure 1.
Compromised Germinal Center Formation and Altered Antibody Affinity Maturation in B Cells Lacking Binding of WIP to Actin
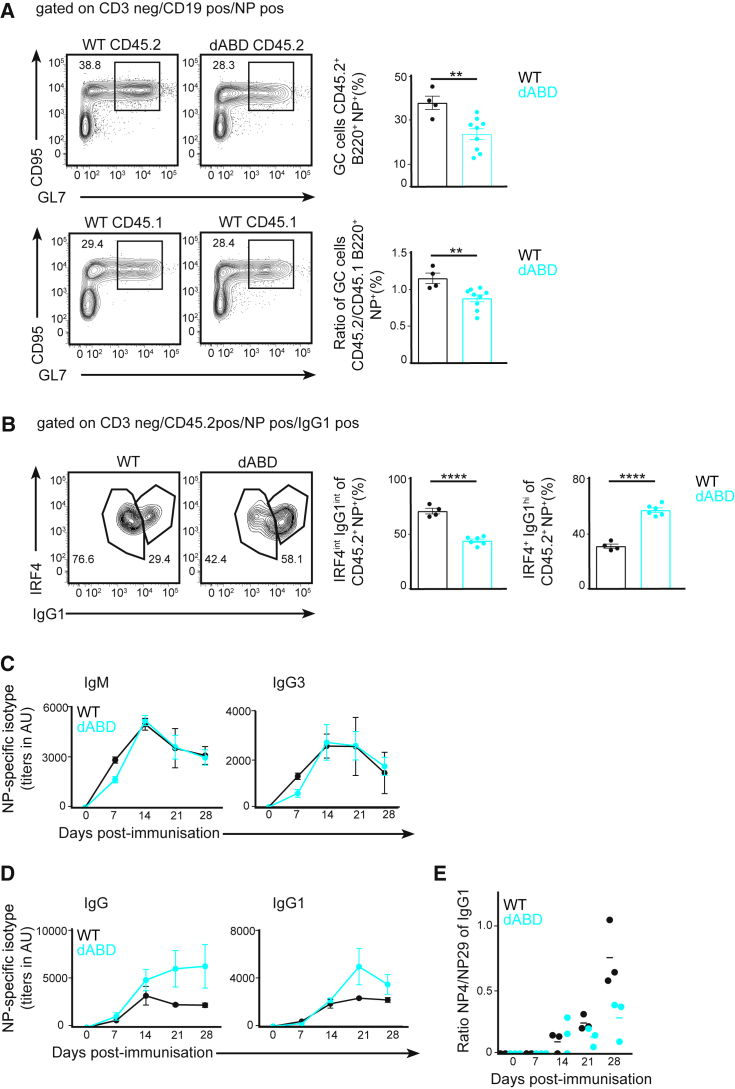
(A and B) Lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipients were reconstituted for 10 weeks with mixtures of 50% WT CD45.1+ BM and 50% WT or WIPΔABD CD45.2+ BM, immunized with NP-KLH in alum and spleens of chimeras analyzed by flow cytometry at day 13. Data (mean ± SEM) are representative of two independent experiments with at least 4 mice per group. (A) CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ NP-specific GC B cells (B220+, NP+, GL7+, and CD95+) are shown. Graphs on the right indicate the percentages of CD45.2+ GC cells and the CD45.2/CD45.1 ratio of GC B cells. (B) CD45.2+, NP-specific, and IgG1+ cells expressing the transcription factor IRF4 are shown. Graphs on the right indicate the percentages of IRF4intIgG1int and IRF4+IgG1hi cells.
(C–E) JHT-WT or JHT-WIPΔABD mixed BM chimeras were immunized with NP-KLH in alum. NP29-specific IgM and IgG3 (C) and IgG and IgG1 (D) antibodies in the sera of immunized chimeras were determined at the indicated time points by ELISA. Affinity maturation (expressed as the ratio of NP4 to NP29 ELISA titers of IgG1 antibodies) is shown in (E). Data (mean ± SEM) are representative of two independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group.
See also Figure S1.