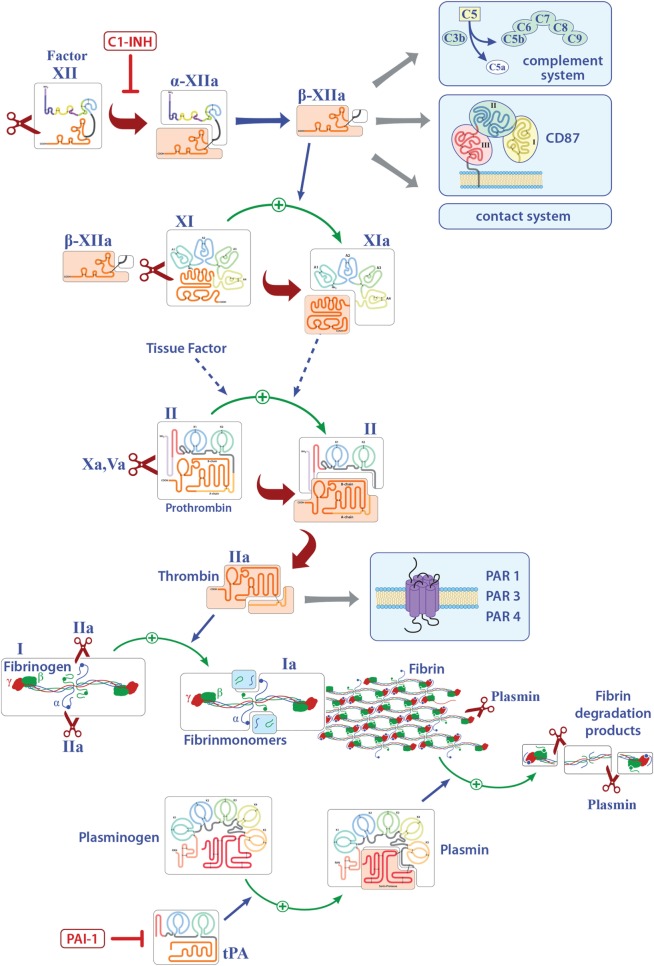
Figure 1.
Overview of the known pathways activated by factor XII (FXII) and the extrinsic coagulation system. Only factors that are involved in inflammation are shown. Activated FXII leads to the cleavage of factor XI, activates the intrinsic, the contact, and complement systems and can bind to CD87. Tissue factor finally leads to the release of thrombin (FIIa) that can directly bind several receptors and activates fibrinogen to fibrin. Deposition of fibrin is regulated by plasmin. Abbreviations: C1-INH, serine protease C1 inhibitor; CD87, urokinase-type plasminogen-activator receptor; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; PAI-1, plasminogen-activator inhibitor 1; PAR, protease-activated receptor.