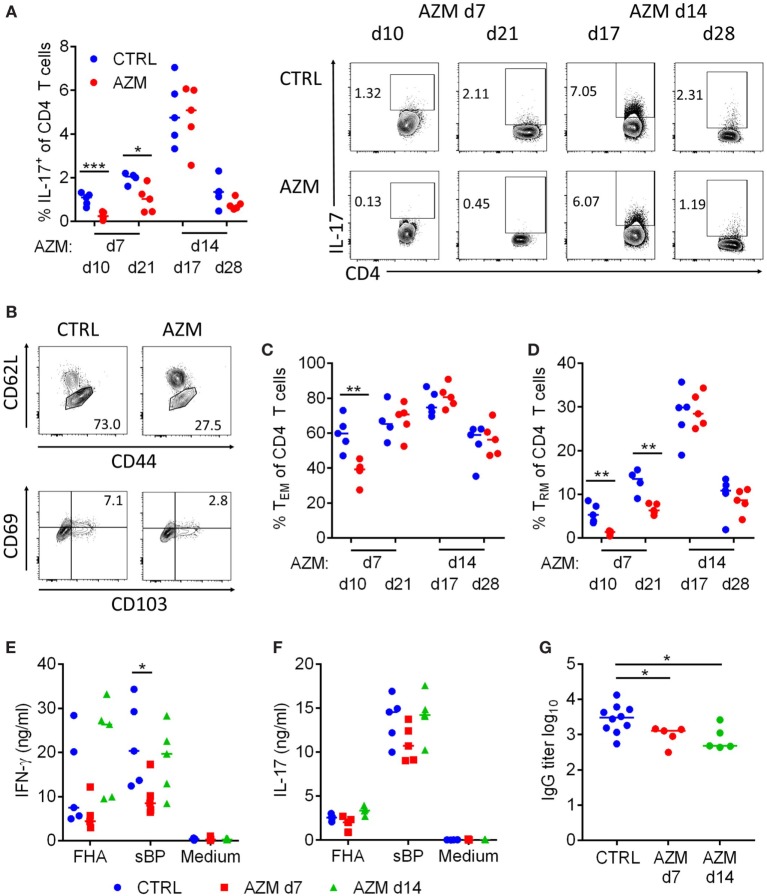
Figure 3.
Azithromycin (AZM) treatment at 7 days post Bordetella pertussis challenge modulates induction of T cell and antibody responses. CD4 T cells in lung digests were characterized by flow cytometry. The percentage of IL-17-producing cells in the CD4 population was analyzed via intracellular cytokine staining 3 and 14 days after treatment. Representative dot plots of the CD4+ population are shown (A). TEM (CD62Llow CD44+) (C) and tissue-resident memory T (TRM) (CD62Llow CD44+ CD69+ CD103+) (D) were analyzed 3 and 14 days after treatment. (B) Upper panels show representative dot plots of the CD4+ population on day 10, lower panels show representative dot plots of the TEM population on day 10. Splenocytes were obtained 28 days post challenge (dpc) and stimulated with filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA) or sBP for 72 h. IFN-γ (E) and IL-17 (F) production in the supernatants were determined via ELISA. Serum was collected from mice on 28 dpc and FHA-specific total IgG serum titers were determined via ELISA (G). (A,C–G) Horizontal lines indicate mean. Significances were determined via t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.