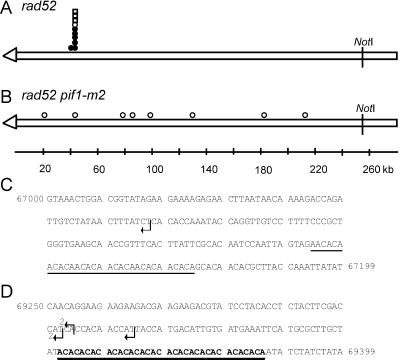
Figure 4.
Positions of de novo telomere addition sites internal to URA3. The ∼255-kb NotI fragment from the left end of the test chromosome is depicted in A and B. The open arrowhead represents the telomere. The symbols indicate the sites where new telomeres were added in independent stabilized clones isolated in the rad52 strain (A) or the rad52 pif1-m2 strain (B). Circles are clones isolated in the experiments used to determine the frequencies of stabilization reported in Supplementary Table 1A. Squares indicate clones isolated in independent stabilization experiments. Open symbols denote clones whose positions were determined solely by PFGE and Southern analysis. Closed symbols denote the positions of clones that were mapped precisely by DNA sequencing; the sequence at these sites is presented in C and D. C and D are the sequence of two sites ∼50 kb from the left telomere of chromosome VII. Arrows indicate the sites of telomere addition in five independent stabilized clones isolated in the rad52 strain. The sequence in C is 200 base pairs, starting at base pairs 67,000 from the left telomere of chromosome VII (all sequence coordinates are from the Saccharomyces genome database; http://genome-www.stanford.edu/Saccharomyces). A 31-base pair CA-rich tract that resembles but does not match the consensus sequence for telomeric DNA is underlined. The dotted line denotes a 7-base pair stretch of telomere-like DNA. (D) Shows 150 base pairs, starting at base pairs 69250. The (CA)17 tract is in bold and underlined. There were no other stretches of 6 bps or greater of telomere-like DNA in the 2.4-kb segment of chromosome VII between coordinates 67,000–69,400.